| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
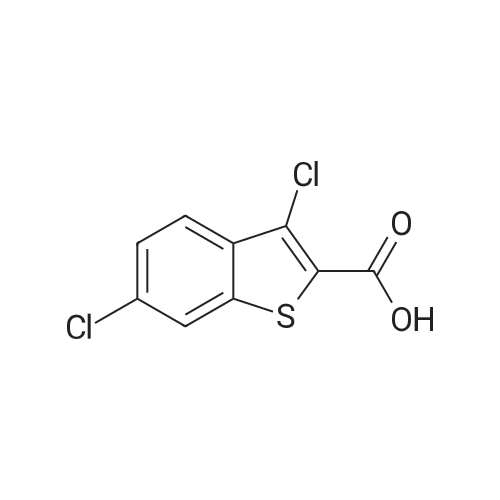
| 描述 | Impaired branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) catabolism plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of metabolic and neurological diseases. The mitochondrial branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC) kinase (BDK) inhibitors that augment BCKDC flux have been shown to reduce BCAA concentrations in vivo. BT2 is a novel BDK inhibitor with an IC50 value of 3.19 μM. In wild-type MEF cells, BT2 robustly stimulated BCKDC activity at concentration of 40 μM for 48 h. Administration of BT2 at 20 mg/kg/day to wild-type mice for 1 week led to nearly complete dephosphorylation and maximal activation of BCKDC in heart, muscle, kidneys, and liver with reduction in plasma BCAA concentrations[3]. | ||
| 作用机制 | Mechanism: BT2 binds to an allosteric site in the N-terminal domain of each monomer in homodimeric BDK[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
4.05mL 0.81mL 0.40mL |
20.23mL 4.05mL 2.02mL |
40.47mL 8.09mL 4.05mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|