| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
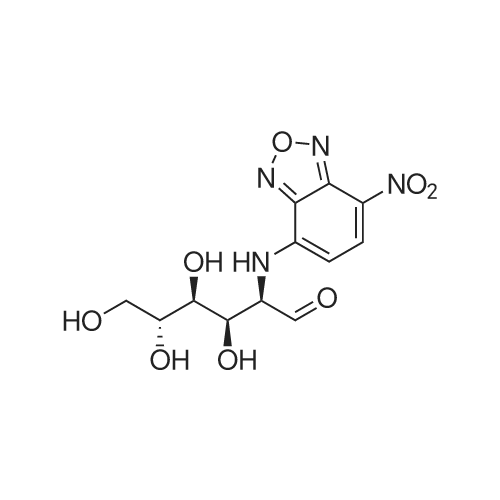
| 描述 | 2-NBDG, a fluorescent D-glucose analog, is a fluorescent indicator for monitoring glucose uptake into living cells. Ex: 467 nm; Em 542 nm. It has since been demonstrated in living mammalian cells that the uptake of 2-NBDG takes place through glucose transporters (GLUTs) in a concentration-, time- and temperature-dependent manner. A short-period application of 2-NBDG produced a remarkable increase in the fluorescence intensity in COS-1 cells over-expressing GLUT2, whereas the increase was barely detectable in mock-transfected cells. In mouse insulin-secreting clonal MIN6 cells, uptake was inhibited by cytochalasin B, a specific blocker for GLUTs, and by D-glucose in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Circulating breast cancer cells with increased uptake of fluorescent 2-NBDG were detected in mice bearing human breast cancer xenograft tumors by fluorescence imaging, suggesting clinical use of 2-NBDG as a tracer for fluorescence imaging of hypermetabolic circulating breast cancer cells[2]. 2-NBDG was continuously injected via the tail vein. Brain glucose metabolism was subsequently monitored by fluorescence imaging of 2-NBDG. The initial uptake rate of 2-NBDG at the injection site of 4-aminopyridine significantly exceeded that of the control injection site, which indicated local hypermetabolism induced by seizures. 2-NBDG can be used for localizing epileptic foci[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.92mL 0.58mL 0.29mL |
14.61mL 2.92mL 1.46mL |
29.22mL 5.84mL 2.92mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|