| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
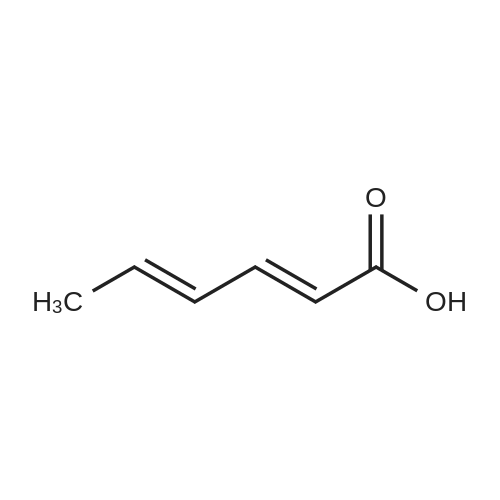
| 描述 | Sorbic acid (Sorbate ) generally is an effective inhibitor of most molds and yeasts and some bacteria. Environmental factors such as pH, water activity, temperature, atmosphere, microbial load, microbial flora and certain food components can influence the effectiveness of sorbate. Strains of microorganisms resistant to sorbate exist and therefore are common causes of food spoilage. Some molds and bacteria are able to degrade sorbate[1]. Sorbate and benzoate showed inhibitory activities against C. perfringens in the rich medium, no such effect was observed in cooked chicken meat[2]. Sorbate concentration decreased during film storage due to its oxidative degradation. Active films resulted more yellow and less transparent than films without sorbate. The minimum inhibitory concentration of sorbate resulted 0.3%, regardless of the starch type and the formulation pH[3]. | ||
| 临床研究 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT号 | 适应症或疾病 | 临床期 | 招募状态 | 预计完成时间 | 地点 |
| NCT01898091 | - | Completed | - | - | |
| NCT01898091 | Oral Mucositis | Phase 2 | Completed | - | United States, South Carolina ... 展开 >> Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, South Carolina, United States, 29425-9170 收起 << |
| NCT02011269 | Plaque Psoriasis | Phase 2 | Withdrawn(Study not conducted) | - | - |
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
8.92mL 1.78mL 0.89mL |
44.59mL 8.92mL 4.46mL |
89.18mL 17.84mL 8.92mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|