| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
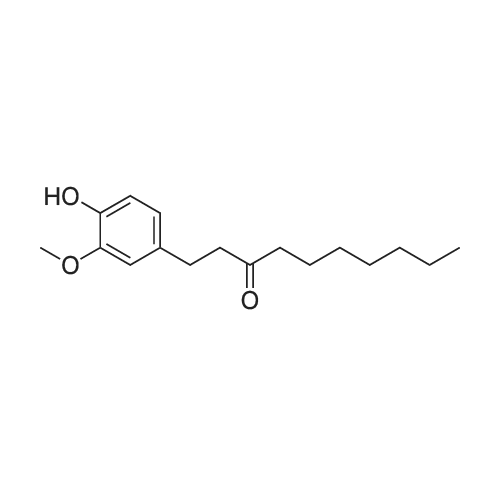
| 描述 | Paradols are non-pungent and biotransformed metabolites of shogaols and reduce inflammatory responses as well as oxidative stress as shogaols. Pretreatment with 6-paradol (paradol derivatives) reduced neuroinflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglia by a concentration-dependent manner[3]. [6]-Paradol, a pungent phenolic compound present in certain Zingiberaceae plants, is known to have antimicrobial and analgesic activities. [6]-Paradol can attenuate promotion of skin carcinogenesis and TPA-induced ear edema in female ICR mice, and to induce apoptosis in cultured human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells[4]. Once-daily administration of 6-shogaol and 6-paradol (5 mg/kg/day, p.o.) to symptomatic EAE (experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis) mice significantly alleviated clinical signs of the disease along with remyelination and reduced cell accumulation in the white matter of spinal cord[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.59mL 0.72mL 0.36mL |
17.96mL 3.59mL 1.80mL |
35.92mL 7.18mL 3.59mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|