| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
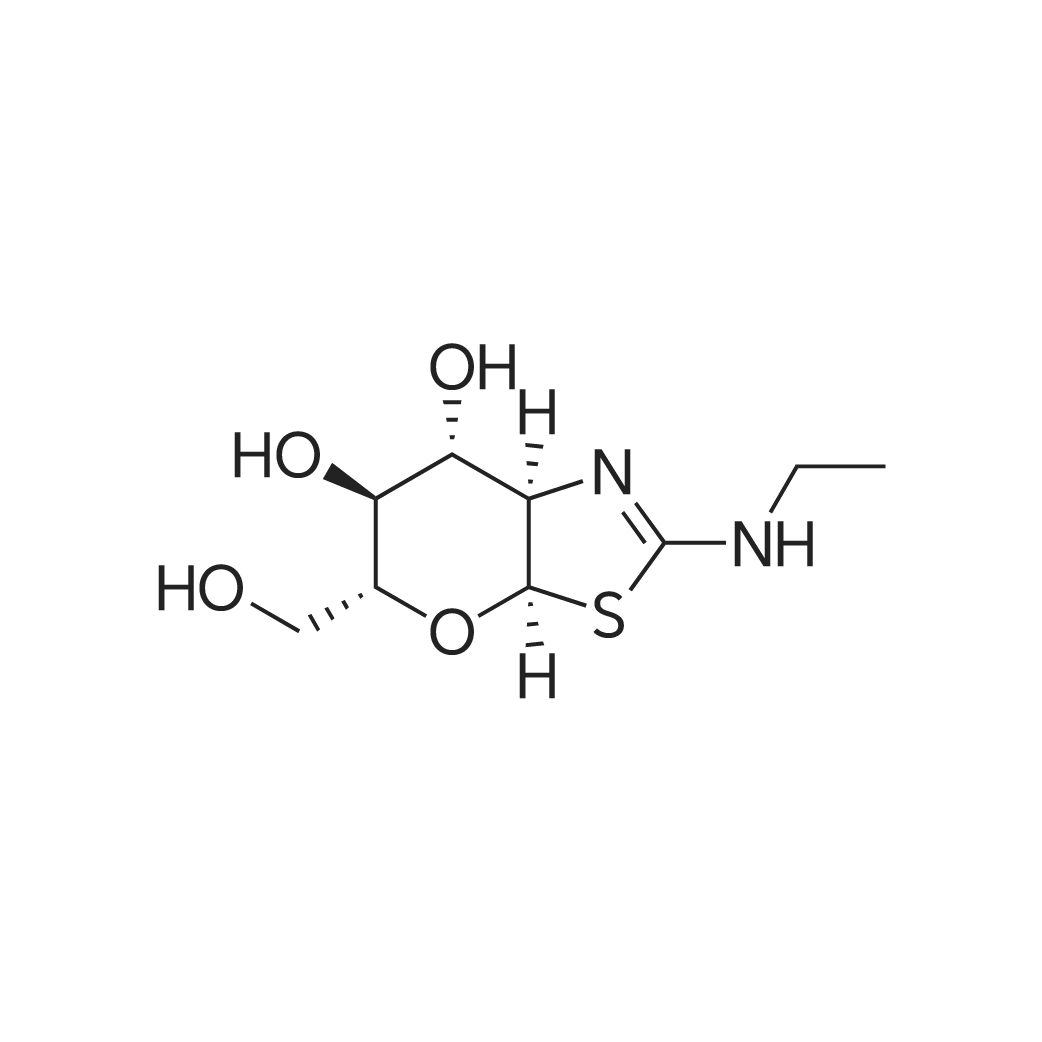
| 描述 | Oligomerization of tau is a key process contributing to the progressive death of neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Tau is modified by O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc), and O-GlcNAc can influence tau phosphorylation in certain cases. Thiamet G is a selective and potent inhibitor of O-GlcNAcase (OGA), which can remove O-GlcNAc from modified proteins, with Ki of 20 nM for human OGA[3]. In Pc-12 cells, Thiamet G increased the level of O-GlcNAc by inhibiting OGA with an EC50 value of 30 nM. Thiamet G (100 mM) decreased tau phosphorylation at Ser396, Thr231, Ser422, and Ser262 by 2.1, 2.7, 1.2, and 1.3 times, respectively. Thiamet G was injected intravenously at a dose of 50 mg/kg in rats. It could increase the O-GlcNAc level in brain in a dose- and time-dependent manner and reduce tau phosphorylation in brain after crossing the blood brain barrier[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
4.03mL 0.81mL 0.40mL |
20.14mL 4.03mL 2.01mL |
40.27mL 8.05mL 4.03mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|