| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
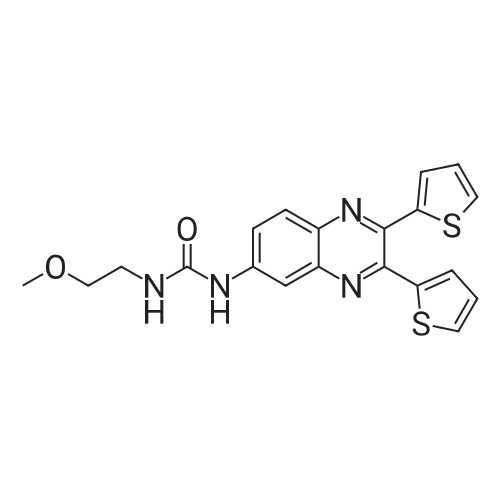
| 描述 | Acetyl-CoA represents a central node of carbon metabolism that plays a key role in bioenergetics, cell proliferation and the regulation of gene expression. The nucleocytosolic acetyl-CoA synthetase enzyme, ACSS2, supplies a key source of acetyl-CoA for tumors by capturing acetate as a carbon source[1]. ACSS2 inhibitor (quinoxaline) is a reversible inhibitor of acetate-dependent acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 (ACSS2) with IC50 of ~ 600 nM. This quinoxaline compound inhibits the ability of HepG2 cells to incorporate [14C]acetate into lipids with IC50 of 6.8 μM, and also inhibits HepG2 utilization of [14C]acetate for histone acetylation with IC50 of 5.5 μM[1]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.44mL 0.49mL 0.24mL |
12.18mL 2.44mL 1.22mL |
24.36mL 4.87mL 2.44mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|