| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
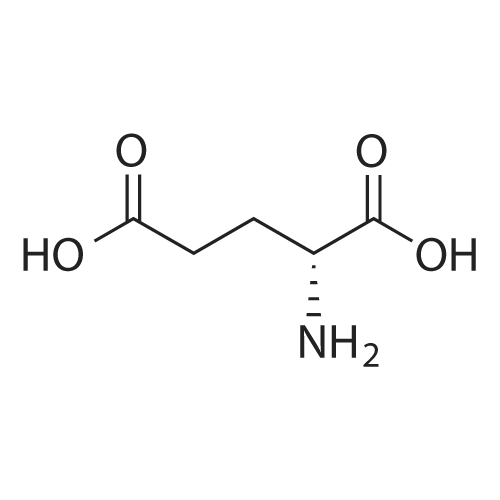
| 描述 | D-glutamic acid is prevalent in mammals, including humans, currently considered potential new physiologically active agents or biomarkers. D-glutamic acid is garnering interest for its role in modulating neuronal transmission and hormone secretion. In mammals, it is exclusively metabolized by the enzyme D-aspartate oxidase.[1]. At a concentration of 4 mg/mL, D-glutamic acid reduces the binding of IgE to peanuts by 75%, whereas D-Asp do not exhibit any inhibitory effect[2]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
6.80mL 1.36mL 0.68mL |
33.98mL 6.80mL 3.40mL |
67.97mL 13.59mL 6.80mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|