| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
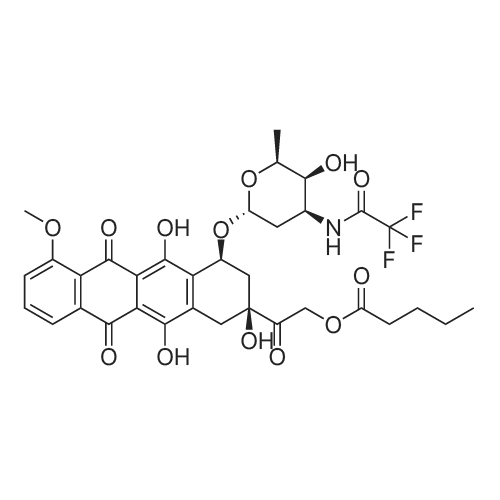
| 描述 | Valrubicin (AD 32) is a chemotherapy agent that inhibits TPA- and PDBu-induced PKC activation with IC50s of 0.85 and 1.25 μM, respectively. Valrubicin competes with the tumor promoter for the PKC binding site, preventing its interaction with phospholipids and binding to PKC [1]. Valrubicin exhibits cytotoxicity against squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cell line colony formation, with IC50s and IC90s of 8.24 ± 1.60 μM and 14.81 ± 2.82 μM for UMSCC5 cells, 15.90 ± 0.90 μM and 29.84 ± 0.84 μM for UMSCC5/CDDP‡ cells, and 10.50 ± 2.39 μM and 19.00 ± 3.91 μM for UMSCC10b cells, respectively. Additionally, the combination of Valrubicin with radiation enhances cytotoxicity [2]. | ||
| 临床研究 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT号 | 适应症或疾病 | 临床期 | 招募状态 | 预计完成时间 | 地点 |
| NCT02256098 | Osteoarthritis Arthritis ... 展开 >> Joint Diseases Musculoskeletal Diseases Rheumatic Diseases 收起 << | Not Applicable | Completed | - | Netherlands ... 展开 >> Medisch Centrum Haaglanden Den Haag, Netherlands, 2501CK Leiden University Medical Center Leiden, Netherlands, 2300RC 收起 << |
| NCT02269254 | Osteoarthritis Arthritis ... 展开 >> Joint Diseases Musculoskeletal Diseases Rheumatic Diseases 收起 << | Not Applicable | Enrolling by invitation | February 2019 | Netherlands ... 展开 >> Leiden University Medical Center Leiden, Netherlands, 2300RC 收起 << |
| NCT00003759 | Bladder Cancer | Phase 2 | Completed | - | United States, Texas ... 展开 >> University of Texas - MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas, United States, 77030-4009 收起 << |
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.38mL 0.28mL 0.14mL |
6.91mL 1.38mL 0.69mL |
13.82mL 2.76mL 1.38mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|