| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
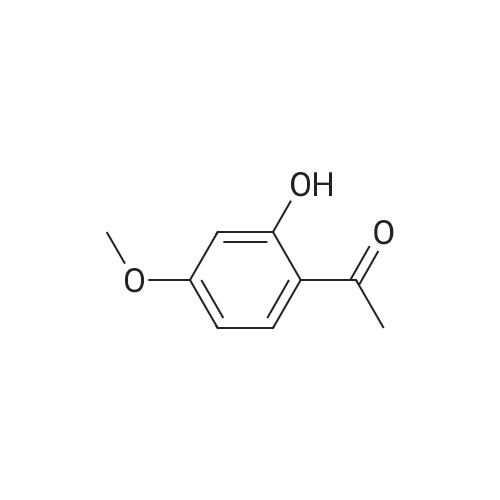
| 描述 | Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is an important enzyme in the metabolism of a wide range of endogenous monoamine neurotrasmitters such as noradrenaline, dopamine, and serotonin (5-HT), and also catalyzes as well the removal of exogenous amines. Paeonol, originated from the traditional Chinese medicine, is a naturally occuring MAO inhibitor with IC50 values of 54.6 μM and 42.5 μM for MAO-A and MAO-B, respectively[7]. Paeonol dose- and time- dependently induced not only antiproliferation activity and apoptosis but also autophagy via blocking the Akt/mTOR pathway in A2780 and SKOV3 cells. In addition, combination treatment with Paeonol and an autophagy inhibitor (3-methyladenine and hydroxychloroquine) showed significant synergetic effects on inhibiting cell viability and promoting apoptosis in vitro and in the A2780 xenograft model, without severe side effects[8]. Paeonol at 50 and 100μM prevented IL-1β-induced inflammatory response by inhibiting numerous factors of osteoarthritis(OA), including IL-6, TNF-a, NOX2, PTGS2, NUCB2/nesfatin-1, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, MMP-3/13, degradation of type II collagen, and NF-kB activation through the rescue of IkBa in human primary chondrocytes[9]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
6.02mL 1.20mL 0.60mL |
30.09mL 6.02mL 3.01mL |
60.18mL 12.04mL 6.02mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|