| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
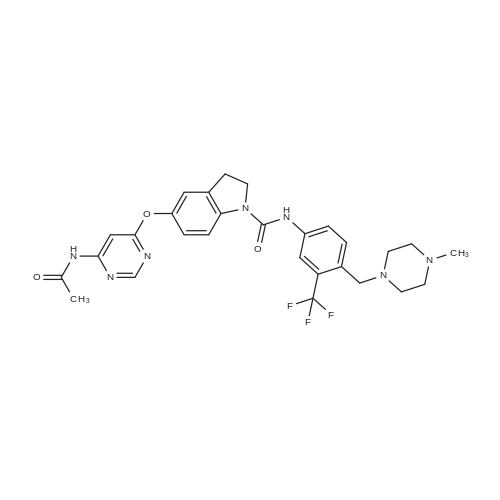
| 描述 | The receptor tyrosine kinase RET (REarranged during Transfection) is activated by its ligand glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). RET signalling is involved in a diverse range of developmental processes including proliferation, migration survival and/or differentiation[3]. BBT594 is a potent RET inhibitor, used for cancer treatment. In human breast cancer MCF7 cells, BBT594 showed the highest suppression of GDNF-induced RET signaling, as assessed by RET, ERK1/2, AKT and ER phosphorylation, compared with sunitinib and cabozantinib. BBT594 treatment ranging in 0-1000 nM blocked the GDNF-mediated enhancement of MCF7-LTED cell viability in 2D culture and 3D colony formation[4]. 100 nM of BBT594 remarkably elevated the antiproliferative effects of letrozole in MCF7-2A cells[5]. BBT594 also acts as type II JAK inhibitor. BBT594 (1 μM, 48h) alone or combined with rapamycin (0.2 μM)/AZD2014 (0.2 μM) induced modest cell apoptosis in 2 P2RY8-CRLF2 samples (CRLF2-re and JAK2 mutation) and significant cell death in IGH-CRLF2 sample ex vivo[6]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.76mL 0.35mL 0.18mL |
8.78mL 1.76mL 0.88mL |
17.56mL 3.51mL 1.76mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|