| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
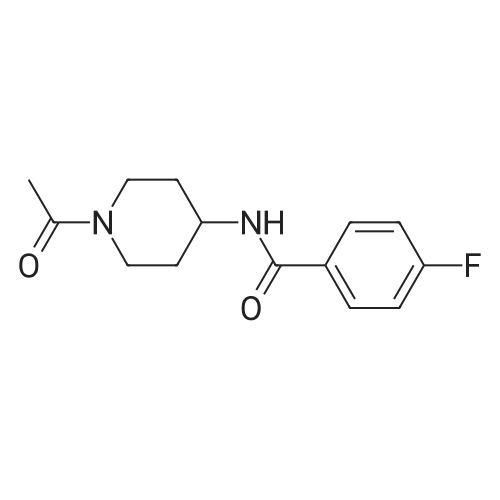
| 描述 | Somatostatin is a neuropeptide that plays an important role in learning and memory. The impairment of somatostatin-mediated neurotransmission is associated with dementia in Alzheimer's disease. FK962 is an anti-dementia compound that facilitates somatostatinergic nerve activity in hippocampal neurons. FK962 at a concentration of 10-7M significantly enhanced somatostatin release evoked by 50mM K+ stimulation from rat hippocampal slices (by 67% compared to the group without FK692). The co-treatment of 10-8M FK962 and somatostatin reversed somatostatin-induced inhibition of Ca2+ currents. Administration of FK962 (0.032-3.2mg/kg) prolonged the retention latency in scopolamine-treated rats with a bell-shaped dose-response curve with the maximal effect observed at 0.32mg/kg. The percentage of rats reaching criteria, which was another index of memory, was increased by FK962 treatment with a bell-shaped dose-dependency and the maximal effect was at 0.32mg/kg. FK962 treatment at 0.032 to 3.2mg/kg also restored the retention latency in nucleus basalis magnocellularis-lesioned rats and aged rats (26-27 months old)[1]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.78mL 0.76mL 0.38mL |
18.92mL 3.78mL 1.89mL |
37.84mL 7.57mL 3.78mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|