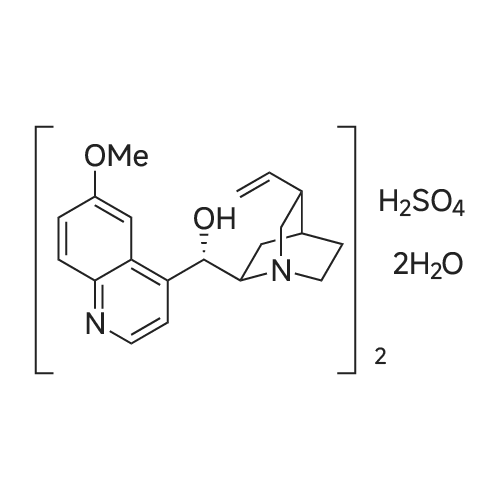
 |
同义名 : | 硫酸奎尼丁 |
| CAS号 : | 6591-63-5 | |
| 货号 : | A953863 | |
| 分子式 : | C40H54N4O10S | |
| 纯度 : | 98% | |
| 分子量 : | 782.943 | |
| MDL号 : | - | |
| 存储条件: |
Pure form Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature In solvent -20°C:3-6个月-80°C:12个月 |
|
| 溶解度 : | - | |
| 动物实验配方: |
| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
| 描述 | Quinidine Sulfate (quinidine) is a non-specific ionic channel blocker that inhibits all the membrane currents in the atrioventricular node including the acetylcholine-activated K+ current. Voltage clamp experiments revealed that 5 mumol/l quinidine reduced the slow inward current, hyperpolarization-activated inward current, and delayed rectifying K+ current, through its membrane actions[1]. Quinidine Sulfate, which has antiarrhythmic activity, greatly enhanced the cytotoxicity of vincristine (VCR) in tumor cells and especially in VCR-resistant sublines of P388 leukemia (P388/VCR) and human myelogenous leukemia. A nontoxic concentration of quinidine increased VCR cytotoxicity in these resistant tumor cells about 50 to 80 times, and the drug in combination with VCR could completely reverse VCR resistance of these cell lines. Quinidine also enhanced the cytotoxicity of Adriamycin, especially in the Adriamycin-resistant subline of P388 leukemia; this enhancement (8-fold) was less than that of VCR toxicity in the VCR-resistant tumor line. When administered daily for 10 days with VCR, quinidine at doses of 50 to 125 mg/kg significantly enhanced the chemotherapeutic effect of VCR in P388/VCR-bearing mice. Quinidine increased the cellular levels of VCR and daunomycin in VCR-resistant sublines of mouse and human tumors and the ADM-resistant mouse tumor line in vitro, respectively. Quinidine also enhanced the cellular accumulation of VCR in P388/VCR cells in vivo[2]. Quinidine sulphate (6 mM) significantly prolonged repolarization of the ventricular action potential. Quinidine reduced the amplitude of a transient outward current, and accelerated its rate of decay by approximately 4 fold at membrane potentials between 0 to +50 mV. Quinidine blocks outward K+ currents in rat ventricular cells[3]. Quinidine treatment resulted in a > 50% seizure reduction in 20% of patients, with rare patients achieving transient seizure freedom[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.28mL 0.26mL 0.13mL |
6.39mL 1.28mL 0.64mL |
12.77mL 2.55mL 1.28mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|

