| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
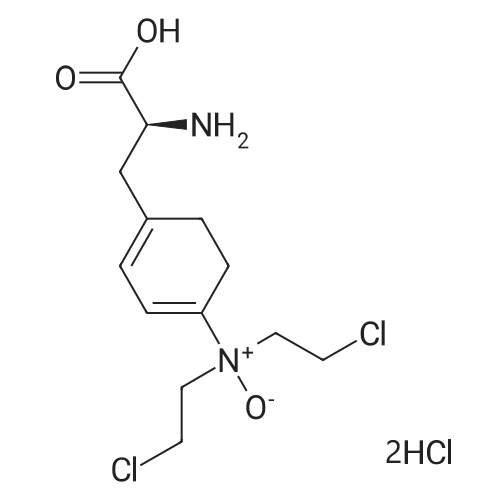
| 描述 | HIF-1α is constitutively expressed subunit of HIF-1 mediating the cellular response to hypoxia, which can be rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-26S proteasome pathway under conditions of normoxia. PX-478 target on HIF-1α, which can selectively inhibit the hypoxia-induced increase in HIF-1a protein. Treatment with PX-478 for 16h can inhibit nuclear HIF-1αprotein level in cell lines under hypoxic (1% O2, 5%CO2, 94% N2) compared with cells under normoxia (air, 5% CO2) with IC50 values for PC-3 prostate cancer cells of 3.9 ± 2.0 μM, MCF-7 breast cancer cells of 4.0 ± 2.0 μM, HT-29 colon cancer cells of 19.4 ± 5.0 μM, Panc-1 pancreatic cancer cells of 10.1 ± 1.9 μM and BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells of 15.3 ± 4.8 μM, without affection on levels of HIF-1βprotein. Meanwhile, PX-478 treatment also significantly decreased the activity of a HIF-1 (measured by transiently transfected HIF-1 reporter), as well as hypoxia-induced expression of VEGF, a HIF-1-regulated protein, in MCF-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner (0 - 25 μM, for 16h) but did not affect basal levels of VEGF formation under normoxic conditions[1]. Treatment with PX-478, i.p., at dose of 75 or 100 mg/kg/day repressed tumor growth in female SCID mice were implanted, s.c., with SHP-77 human small cell lung cancer cells. Also treatment with PX-478, i.p., at dose of 100mg/kg/day suppressed tumor growth in male SCID mice implanted s.c. with PC-3 prostate cancer cells[2]. Up to now, phase 1 studies of PX-478 treatment for advanced solid tumors and lymphoma have been completed (see https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/) | ||
| 作用机制 | The action of PX-478 on HIF-1αmay due to: 1. Modulation of HIF-1αubiquitination; 2. Inhibition on HIF-1α transcription; 3. Inhibition on HIF-1α translation. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.52mL 0.50mL 0.25mL |
12.62mL 2.52mL 1.26mL |
25.24mL 5.05mL 2.52mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|