| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
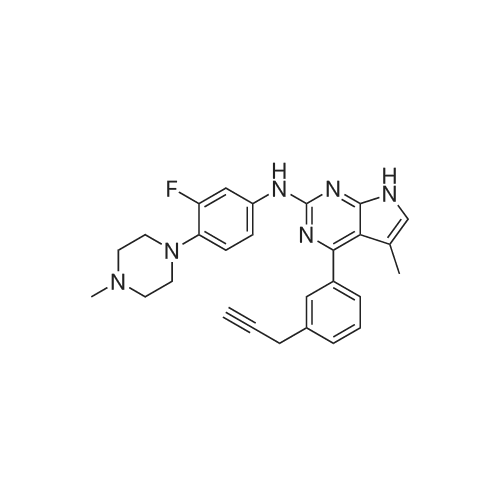
| 描述 | The AXL protein, classified as a RTK (Receptor tyrosine kinase), belongs to the TAM (TYRO3, AXL, and MER) subfamily. Overexpression or overactivation of the AXL has been correlated with the promotion of multiple tumorigenic processes. SGI-7079 is a relatively potent AXL inhibitor (IC50 = 58 nM, in cell-free assays) in preclinical development. It inhibits GAS6-stimulated AXL signaling in inflammatory breast cancer cells (IC50 < 1 μM), resulting in decreased cell proliferation and invasion[3]. Mesenchymal cell lines expressing Axl were highly sensitive to SGI-7079 alone. In a mouse xenograft model of NSCLC (non-small cell lung cancer), SGI-7079 inhibited tumor growth in a dose dependent manner, and at the maximum dose, inhibited tumor growth by 67%, compared to control. Notably, SGI-7079 + erlotinib (25/100 mg/kg) reduced the tumor growth by 82%[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.20mL 0.44mL 0.22mL |
10.98mL 2.20mL 1.10mL |
21.95mL 4.39mL 2.20mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|