| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
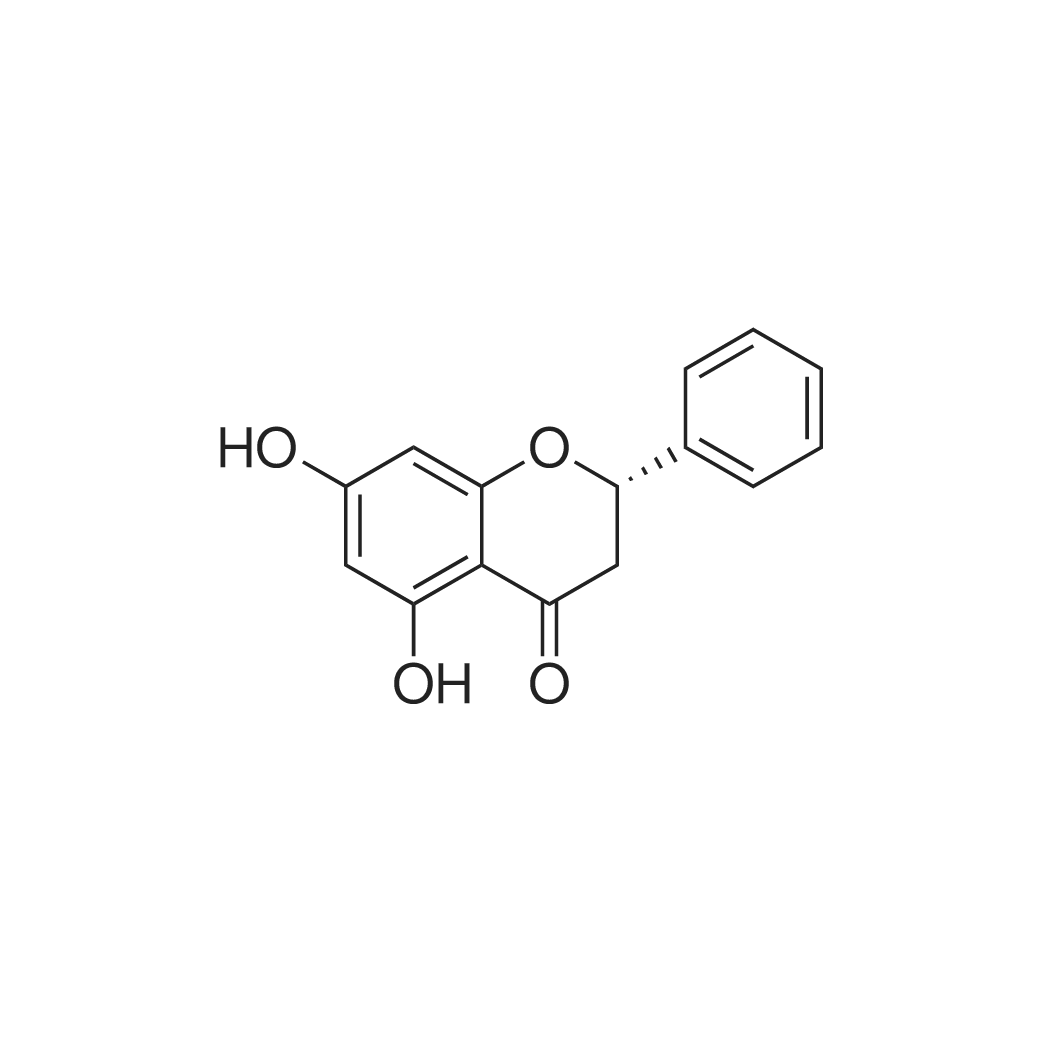
| 描述 | (+)-Pinocembrin 5, 7- dihydroxy flavanone) is the most abundant chiral flavonoid found in propolis, exhibiting antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Pinocembrin inhibits HDC activity and histamine in IgE-sensitized RBL-2H3 in response to dinitrophenol (DNP)-bovine serum albumin (BSA) stimulation. In addition, Pinocembrin mitigated the damage in the mitochondrial membrane, formation of cytoplasmic granules and degranulation as indicated by lower β-hexoseaminidase level[3]. Pinocembrin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy when there is no kidney damage but when it is already present, pinocembrin accelerates kidney damage[4]. Pinocembrin can reduce nerve damage in the ischemic area and reduce mitochondrial dysfunction and the degree of oxidative stress. Pinocembrin can be absorbed rapidly in the body and easily cross the blood-brain barrier. In addition, the absorption/elimination process of pinocembrin occurs rapidly and shows no serious accumulation in the body[5]. In vivo, pinocembrin dose-dependently reduced lesion volume by ∼47.5% and reduced neurologic deficits of mice at 72h after collagenase-induced ICH (intracerebral hemorrhage). The optimal dose of pinocembrin (5mg/kg) suppressed microglial activation as evidenced by decreases in CD68-positive microglia and reduced proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6[6]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.90mL 0.78mL 0.39mL |
19.51mL 3.90mL 1.95mL |
39.02mL 7.80mL 3.90mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|