| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
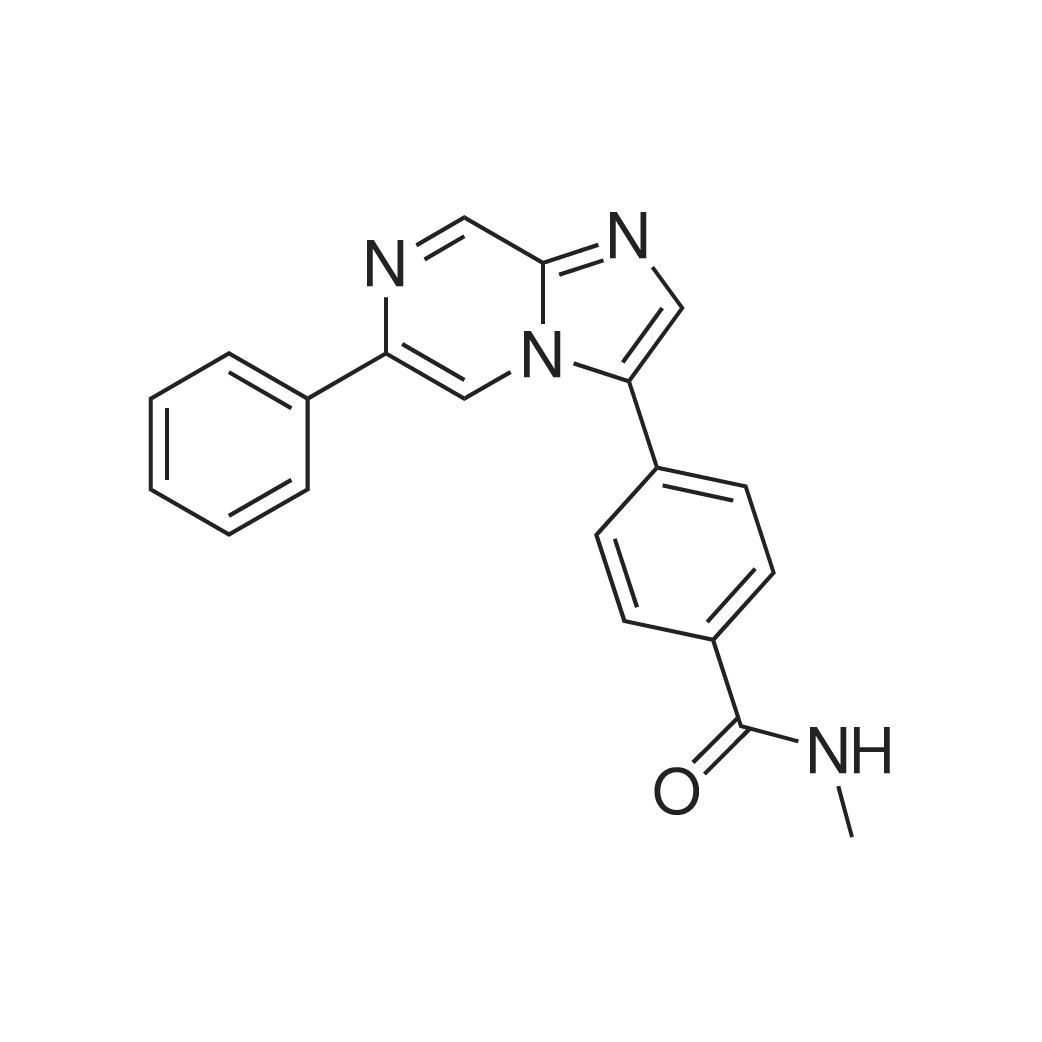
| 描述 | Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) protein is a critical kinase that responds to DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced by cellular exposures to ionizing radiation (IR) and certain intrinsic stimuli. ATM is an ATP-dependent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase (PIKK) serine/threonine protein kinase related to ATR, DNA-PKcs, mTOR, SMG1, and the nonenzymatic TRRAP within this enzyme family[1]. AZ32 is an orally bioavailable and blood-brain barrier-penetrating ATM inhibitor with an IC50 of <6.2 nM for ATM enzyme, and an IC50 of 0.31 μM for ATM in cell[1]. AZ32 blocked the DNA damage response and radiosensitized GBM cells in vitro[1]. AZ32, with enhanced blood–brain barrier (BBB) penetration, was highly efficient in vivo as radiosensitizer in syngeneic and human, orthotopic mouse glioma model. In vivo, apoptosis was >6-fold higher in tumor relative to healthy brain after exposure to AZ32 and low-dose radiation. AZ32 is the first ATMi with oral bioavailability shown to radiosensitize glioma and improve survival in orthotopic mouse models. Following a single oral dose of AZ32 (200 mg/kg) in mice, the free-brain concentrations of AZ32 are in excess of the cellular IC50 for approximately 22 hours[1]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.05mL 0.61mL 0.30mL |
15.23mL 3.05mL 1.52mL |
30.45mL 6.09mL 3.05mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|