| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
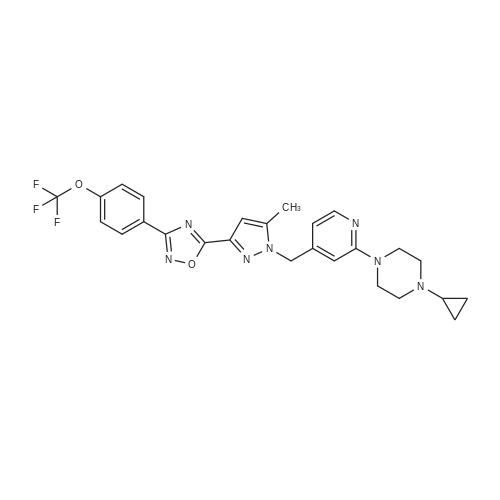
| 描述 | The response of mammalian cells to hypoxia is mediated by a family of transcription factors known as HIF (hypoxia-inducible factors). The subunits of HIF, HIF-1αand HIF-2αare structurally similar and can be degraded rapidly under normoxia through a posttranslational process involving proline hydroxylation in an oxygen dependent manner targeting HIF proteins to the VHL ubiquitination complex for final degradation by the proteasome system. BAY 87-2243 is a HIF-1 inhibitor with IC50 value of 0.7nM (measure by luciferase reporter gene). Treatment with BAY 87-2243 (1-100nM) for 16h inhibited HIF-1α and HIF-2αprotein accumulation in a dose-dependent manner in H460 cells under hypoxia (1% pO2) but hypoxia mimetics. Consistent with that, expression of HIF target genes CA9, ADM and ANGPTL4 was suppressed dose-dependently in hypoxic lung cancer cells treated with BAY 87-2243 (10-1000nM) for 16h. The activity of BAY 87-2243 against HIF-1 protein and its target gene depends on intact VHL protein and PHD activity. BAY 87-2243 also functioned as a mitochondrial complex I inhibitor and inhibited mitochondrial oxygen consumption measured by using the oxygen sensitive fluorescence dye LUX-MitoXpress with an IC50 value of ~10 nM. Once daily oral treatment with BAY 87-2243 (0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 mg/kg for 21 days) could inhibit tumor growth dose-dependently in nude mice bearing established H460 human tumor xenografts[1]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.90mL 0.38mL 0.19mL |
9.51mL 1.90mL 0.95mL |
19.03mL 3.81mL 1.90mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|