| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
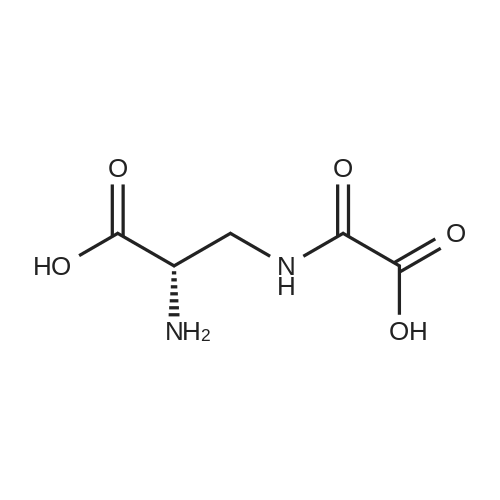
| 描述 | β-ODAP is a strong agonist of AMPA (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-proprionate) receptors, the potency being almost the same as l-glutamate[3]. 3-N-Oxalyl-l-2,3-diaminopropanoic acid (β-ODAP) induces neurolathyrism, a motor neuron disease. β-ODAP had little effect on the glutamate-evoked currents through the expressed NMDA receptor (NR1(A)/NR2A), but showed a weak inhibitory effect on the glycine-modulatory site[4]. L-β-ODAP (β-ODAP) caused a prolonged rise of intracellular Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)]i) in rat spinal cord MNs, and the [Ca(2+)]i accumulation was inversely proportional to the MN's life span[5]. β-ODAP is a neuroexcitatory non-protein amino acid and presents in the seeds of the hardy legume crop grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.), was considered responsible for human lathyrism[6]. beta-ODAP could supply nitrogen for plant growth and seed development, scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), involve in osmotic adjustment as a soluble amino acid, transport zinc-ions as a carrier molecule, and impact nodule development. Although beta-ODAP could induce excitotoxicity by damaging intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and as glutamate analogues, it has medicinal value on hemostasis and anti-tumor[7]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
5.68mL 1.14mL 0.57mL |
28.39mL 5.68mL 2.84mL |
56.78mL 11.36mL 5.68mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|