| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
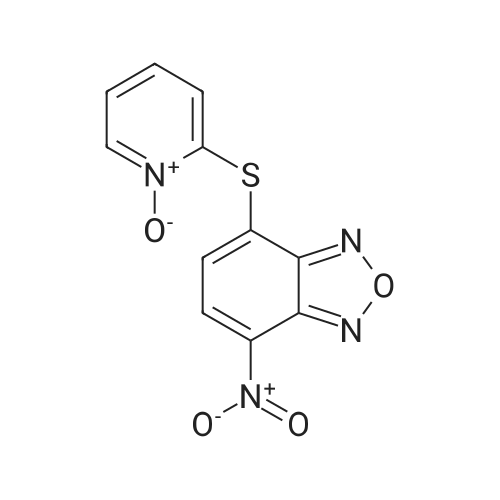
| 描述 | Ligand-dependent activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an essential process governing signal transduction during cell growth, differentiation, survival, and proliferation in physiological conditions. Mutations resulting in overexpression or deregulation of the receptor impair signal transduction, leading to tumor growth. NSC-228155 is an activator of EGFR, which has a positive log P and could enter cells and enhance EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation [1]. It also dose-dependently inhibits KIX-KID interaction with an IC50 of 0.36 μM [2]. The increase in the fluorescence curve at 665 nm was moderately suppressed in the cells exposed to NSC-228155 indicating the generation of H2O2 in redox cycling, which could activate EGFR. NSC-228155 provided high yields of stable SOD1 (superoxide dismutase 1) dimer at concentration of 100 μM for 15 min in MDA MB468 cells, suggesting specific action of NSC-228155 on SOD1. Further studies showed that EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation was enhanced through the action of SOD1 dimer shortly after exposure of cells to 100 μM NSC-228155 for 10 min. Taken together, NSC-228155 primarily induced the formation of a stable SOD1 dimer that was functionally active and led to the accumulation of intracellular H2O2, which in turn activates EGFR [1]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.45mL 0.69mL 0.34mL |
17.23mL 3.45mL 1.72mL |
34.45mL 6.89mL 3.45mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|