| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
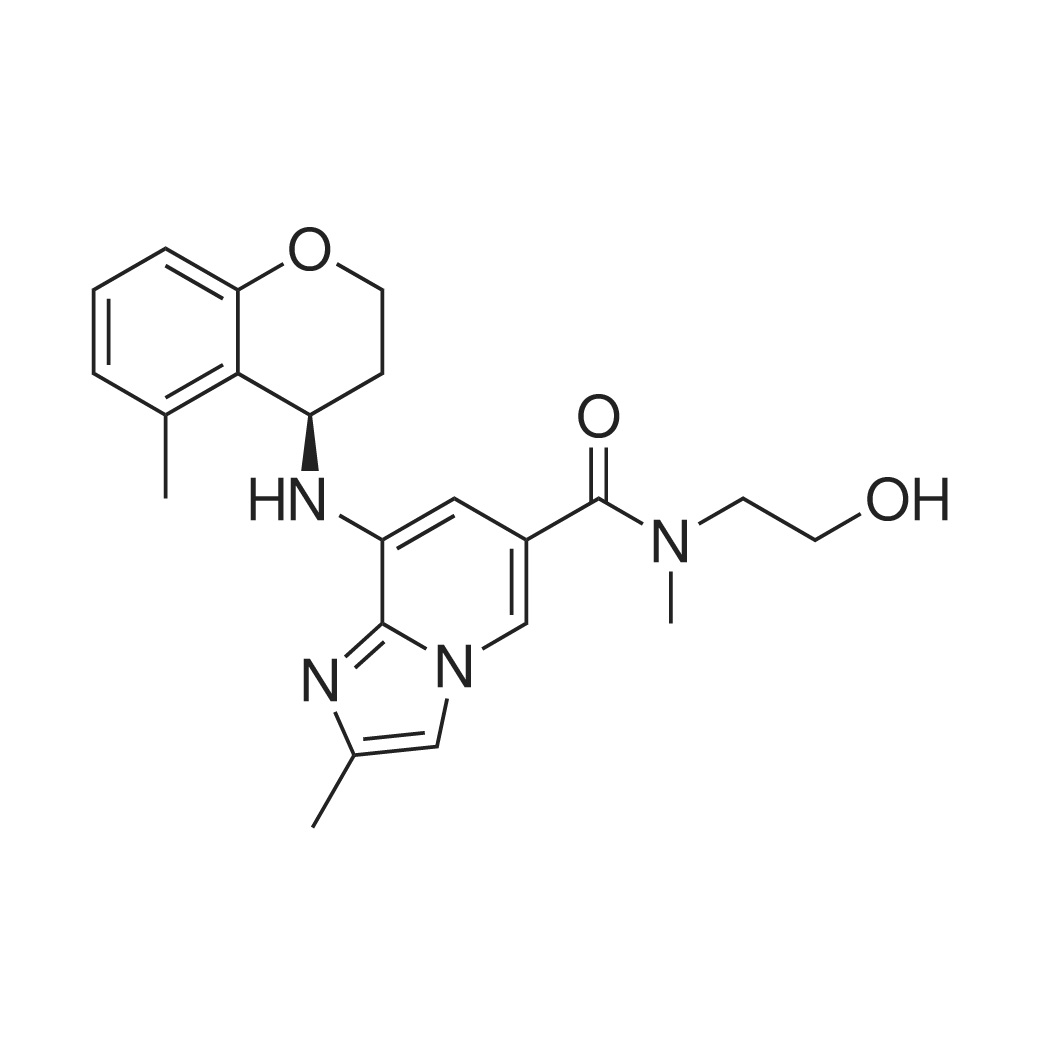
| 描述 | The gastric H+,K+-ATPase, which is responsible for gastric acid secretion, is a P2-type ATPase located in the apical membrane of parietal cells. PF-03716556 is a novel, potent, and selective acid pump antagonist. In the ion-leaky membranes of porcine vesicles, canine vesicles and human recombinant cells, F-03716556 inhibited H+,K+-ATPase activity with pIC50 values of 6.026±0.112, 6.038±0.039 and 6.009±0.209 at pH 6.4, respectively. In the ion-tight membrane of porcine vesicles, PF-03716556 inhibited H+,K+-ATPase activity in a concentration-dependent manner, with a pIC50 value of 7.095±0.077 at pH 7.4. PF-03716556 exhibited high selectivity for the H+,K+-ATPase over the Na+,K+-ATPase. In vivo, administration of PF-03716556 inhibited gastric acid secretion in a dose-dependent manner over concentrations ranging from 1 to 10 mg/kg in Ghosh-Schild rats and 0.3 to 3 mg/kg in Heidenhain Pouch Dogs, respectively[2]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.54mL 0.51mL 0.25mL |
12.68mL 2.54mL 1.27mL |
25.35mL 5.07mL 2.54mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|