| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
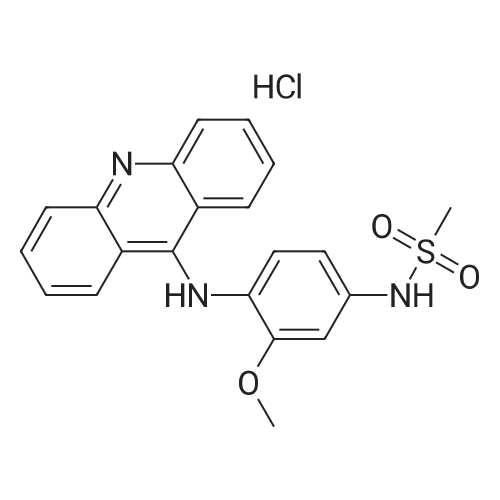
| 描述 | Amsacrine HCl is an inhibitor of topoisomerase II, and acts as an antineoplastic agent which can intercalates into the DNA of tumor cells. Amsacrine blocked HERG currents in HEK 293 cells and Xenopus oocytes in a concentration-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 209.4 nm and 2.0 microm, respectively[3]. During chronic exposure at low concentrations, amsacrine causes cell and nuclear enlargement, lobulation of the nucleus, and nucleolar segregation[4]. In animals treated with different doses of amsacrine (0.5-12 mg kg(-1) ), the frequencies of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes increased significantly after treatment with 9 and 12 mg kg(-1) [5]. Amsacrine abolishes ERK- and Pin1-mediated stabilization of MCL1 and promotes GSK3β-mediated degradation of MCL1, leading to activate mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway in U937 cells[6]. | ||
| 临床研究 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT号 | 适应症或疾病 | 临床期 | 招募状态 | 预计完成时间 | 地点 |
| NCT00002719 | Leukemia Neut... 展开 >>ropenia 收起 << | Phase 3 | Completed | - | Italy ... 展开 >> Azienda Policlinico Umberto Primo Rome, Italy, 00161 收起 << |
| NCT00002658 | Leukemia Neut... 展开 >>ropenia 收起 << | Phase 3 | Unknown | - | United Kingdom ... 展开 >> University of Wales College of Medicine Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom, CF14 4XN 收起 << |
| NCT01324063 | Leukemia | Phase 3 | Completed | - | - |
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.33mL 0.47mL 0.23mL |
11.63mL 2.33mL 1.16mL |
23.26mL 4.65mL 2.33mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|