| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
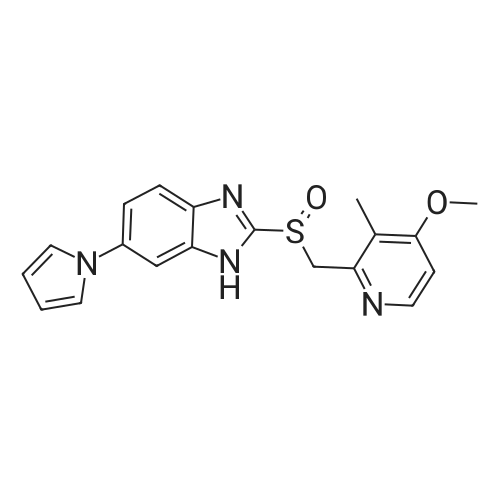
| 描述 | The gastric H+,K+-ATPase, composed of the catalytic α subunit and the structural β subunit, is responsible for gastric acid secretion[1]. Ilaprazole is a novel proton pump inhibitor which inhibits H+,K+-ATPase with an IC50 of 6 μM. Ilaprazole is also a potent T-cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK; playing an indispensable role in the mitosis of cancer cells) inhibitor with a Kd of 111 μM[2]. On cumulation of 14C-aminopyrine in histamine stimulated parietal cells, the IC50 of ilaprazole was 9.0 nM. In rats, ilaprazole given intraduodenally immediately after pylorus ligation, dose-dependently inhibited gastric acid secretion. At 30 mg/kg, it showed 93% and 73% inhibition on acid output and volume compared to control, respectively. In Heidenhain pouch dog, the acid output was blocked dose-dependently by intravenous administration of ilaprazole at doses of 0.3 and 1 mg/kg[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.73mL 0.55mL 0.27mL |
13.64mL 2.73mL 1.36mL |
27.29mL 5.46mL 2.73mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|
|
[1]Shin JM, et al. Gastric H+,K+-ATPase. Compr Physiol. 2011 Oct;1(4):2141-53 |