| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
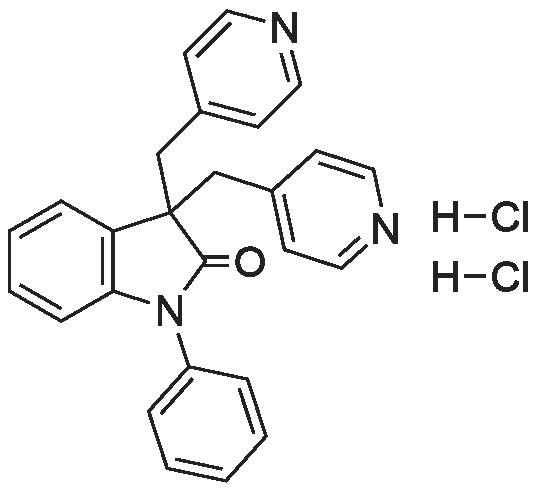
| 描述 | Linopirdine 2HCl (Linopirdine [DuP 996, 3, 3-bis(4-pyridinylmethyl)-1-phenylindolin-2-one]), a putative cognition enhancing drug, increases acetylcholine release in rat brain tissue and improves performance in animal models of learning and memory. Linopirdine was found to block voltage-gated, calcium-activated and leak K+ currents in a dose-dependent manner. Linopirdine was most selective for IM with an IC50 of 2.4 +/- 0.4 microM, followed by IC (measured as a medium afterhyperpolarization tail current, ImAHP) with an IC50 of 16.3 +/- 2.4 microM. Linopirdine selectively blocks IM at concentrations [3]. In addition, linopirdine blocked responses of recombinant alpha9alpha10 nicotinic cholinergic receptors (nAChRs) in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC(50) of 5.2 microM. Block by linopirdine was readily reversible, voltage independent, and surmountable at high concentrations of ACh, thus suggestive of a competitive type of interaction with the receptor[4]. Linopirdine (0.1 and 1 mg/kg) ameliorated the scopolamine-induced deficit, but at doses ranging from 0.01-1 mg/kg, it did not affect passive avoidance retention in normal (untreated) mice. Linopirdine (0.01 and 0.1, but not 1 mg/kg) ameliorated the atropine deficit. In addition, linopirdine (0.1 mg/kg) ameliorated the deficit in cognition-impaired aged rats (23-24 mo), but did not affect unimpaired aged rats. In terms of neurochemical action, linopirdine (1, 10, and 100 microM) produced a concentration-dependent increase in K(+)-evoked ACh overflow from superfused rat hippocampal slices. Also, linopirdine (10 microM) similarly increased ACh release in young control rats and cognition-impaired and nonimpaired aged rats[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.15mL 0.43mL 0.22mL |
10.77mL 2.15mL 1.08mL |
21.53mL 4.31mL 2.15mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|