| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
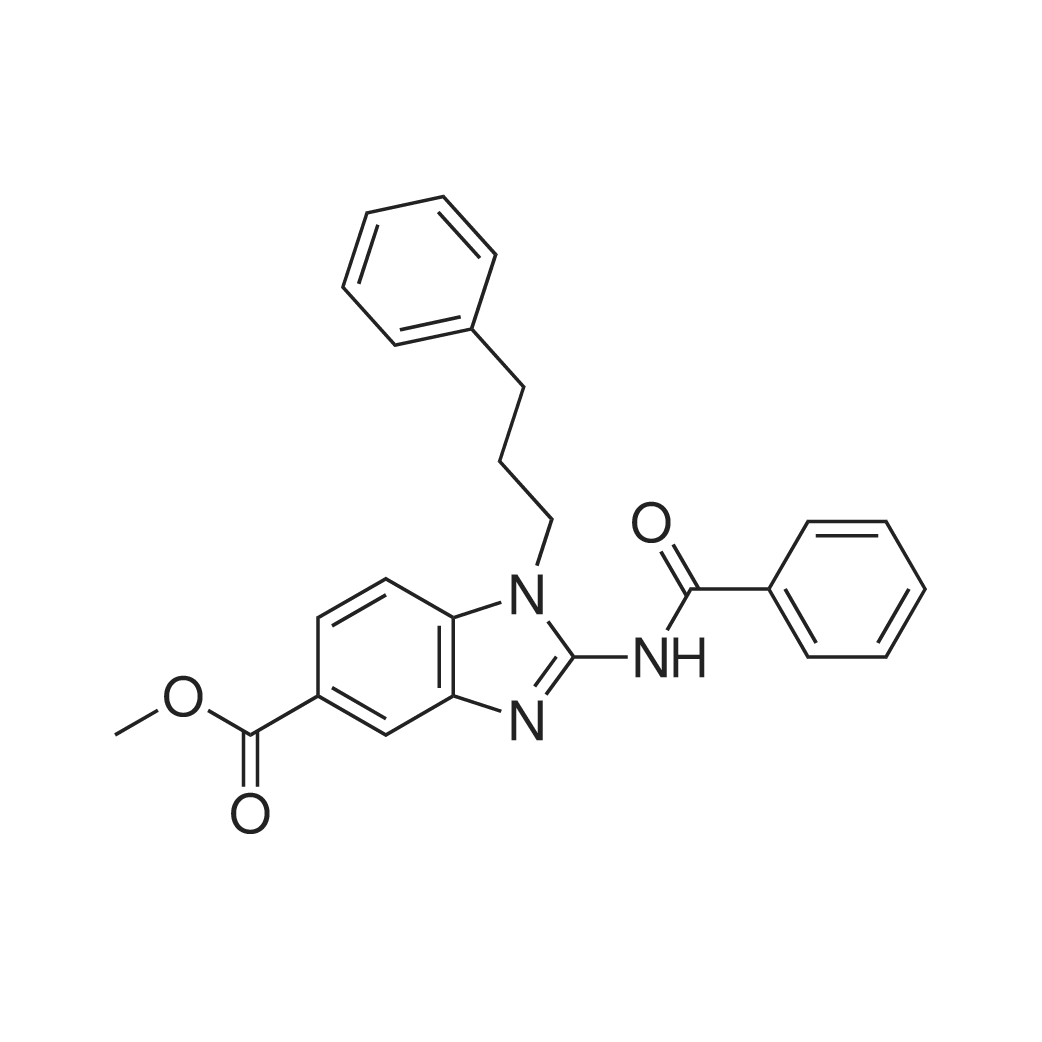
| 描述 | Somatic mutation and amplification of histone methyltransferases are commonly observed in human cancers. BRD4770 is a selective, small-molecule inhibitor of histone methyltransferase G9a. The IC50 value of its active form (BRD9539) for G9a activity in cells is 6.3μM. Treatment of PANC-1 cells with 10μM BRD4770 for 24 hours resulted in a significant decrease in di- and trimethylation levels of H3K9, as well as an increase in monomethylation level. Treatment of PANC-1 cells with 5μM BRD4770 for 24 hours decreased trimethylation level of H3K9 by 23%. The EC50 values of BRD4770 for trimethylated H3K9 in PANC-1 cells were ~5μM. BRD4770-treated PANC-1 cells also showed increased cell population in G2/M and decreased G0/G1 cell fraction compared with DMSO-treated controls[3]. The subcutaneous injection of BRD4770 (10mg/kg, three times per week on days 1, 3, and 5) combined with prexasertib (2mg/kg, injection for three days followed by four-day off) inhibited the growth of subcutaneous L3.6 xenografts in mice[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.42mL 0.48mL 0.24mL |
12.09mL 2.42mL 1.21mL |
24.19mL 4.84mL 2.42mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|