| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
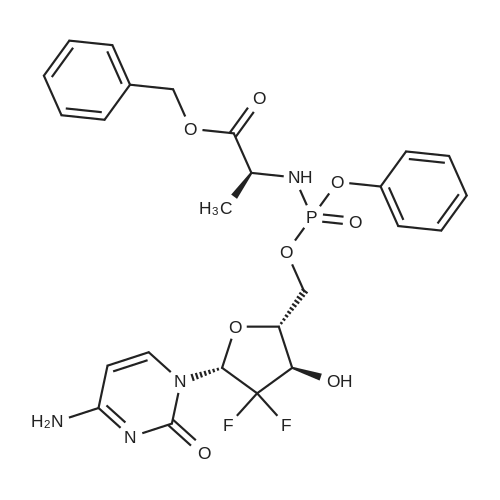
| 描述 | Gemcitabine is a pyrimidine nucleoside analogue commonly used for the treatment of solid tumors. Acelarin is a gemcitabine ProTide with cytotoxic activity against a range of cancer cell lines in vitro, including L1210 (IC50=0.035±0.02μM), CEM (IC50=0.1±0.03μM), MP-2 (IC50=0.44±0.06μM), and BxPC-3 (IC50=0.15±0.04μM). The colorimetric MTT assay showed that acelarin was more cytotoxic than gemcitabine and its activity was not significantly affected by deoxycytidine. In a nude mouse xenograft model of MiaPaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer cells, acelarin at a dose of 0.076mmol/kg achieved significantly greater reduction in tumor volume than gemcitabine on Day 7 after the first administration of the compounds[2]. | ||
| 作用机制 | Acelarin is a gemcitabine ProTide that bears a phosphoramidate moiety on the 5’-carbon of the ribose. It has been shown to resist cytidine deaminase-mediated degradation. Acelarin bypasses deoxycytidine kinase-mediated monophosphorylation and does not rely on the nucleoside transporter human equilibrative nucleoside transporter-1 to exert the anticancer effect.[2] | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.72mL 0.34mL 0.17mL |
8.61mL 1.72mL 0.86mL |
17.23mL 3.45mL 1.72mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|