| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
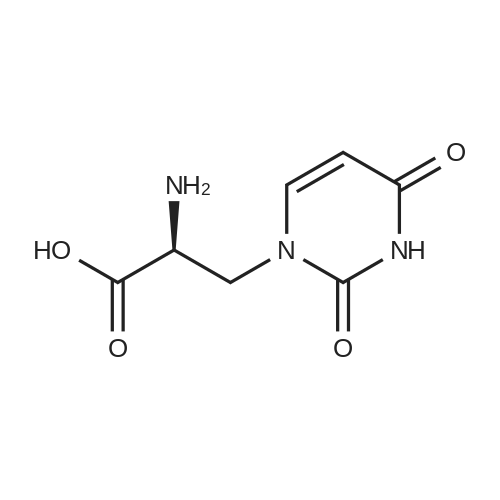
| 描述 | (S) -Willardiine is a potent agonist of AMPA/kainate receptors with EC50 of 44.8 uM. Willardiines produce strikingly different degrees of desensitization: at saturating doses the equilibrium response to the weakly desensitizing agonist (S)-5-iodowillardiine was similar in amplitude to the response to kainate and 10 times larger than the response to the strongly desensitizing agonist (S)-willardiine[3]. In newborn mice (P5, histopathology at P10), local injection of the AMPA receptor agonist S-bromo-willardiine at day 5 after birth induced cortical damage and white matter damage, which was reduced in a dose-dependent manner by the AMPA receptor antagonists[4]. At a concentration of 1.8 mM, Ca2+ inhibited the currents induced by 100 microM willardiine by approximately 50%. Ca2+ inhibition of the willardiine-induced response is concentration dependent[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
5.02mL 1.00mL 0.50mL |
25.10mL 5.02mL 2.51mL |
50.21mL 10.04mL 5.02mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|