| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
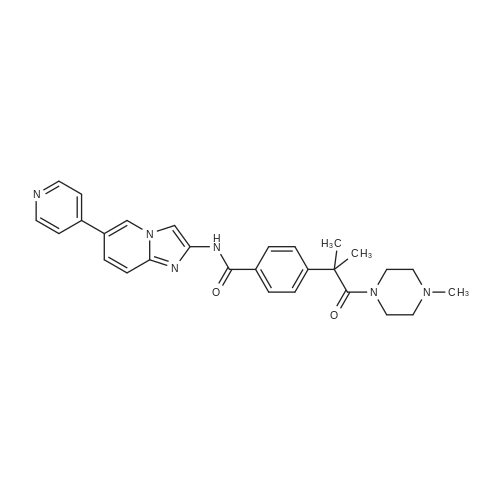
| 描述 | Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a group of multifunctional enzymes consisting of catalytic and regulatory subunits. The regulatory subunit, cyclin, remains dissociated under normal circumstances, and complexation of cyclin with the catalytic subunit of CDK leads to its activation for phosphorylation of protein substrates[2]. CDKs are activated by cyclins, which play important roles in dictating the actions of CDK/cyclin complexes. Cyclin binding influences the substrate specificity of these complexes in addition to their susceptibility to inhibition or degradation. CDK/cyclin complexes are best known to promote cell cycle progression in the mitotic cell cycle but are also crucial for important cellular processes not strictly associated with cellular division[3]. CLK-IN-T3 is a potent inhibitor of CDC-like kinase (CLK) (IC50s: 0.67 nM, 15 nM, and 110 nM for CLK1, CLK2, and CLK3 protein kinases) with anti-cancer activity. CLK-IN-T3 (0.5-1.0 µM; 6 hours) reduces phosphorylation of CLK-targeted SR proteins and CLK proteins increase slightly. CLK-IN-T3 (0.1-10.0 µM; 24 hours) causes mild cell cycle arrest at the G2/M boundary with long-duration (24 h). CLK-IN-T3 has IC50s of 260 nM and 230 nM for DYRK1A and DYRK1B, respectively[4].In embryonic cells, cardiomyocytes, and hearts, the growth and heart rates were significantly slowed in clk-1(-/-) compared with wild-type or heterozygous mouse tissues. Moreover, frequent apoptosis and a significant reduction in mitochondrial functions, including membrane potential and ATP production, were observed in the clk-1(-/-) cells and hearts[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.07mL 0.41mL 0.21mL |
10.36mL 2.07mL 1.04mL |
20.72mL 4.14mL 2.07mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|