| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
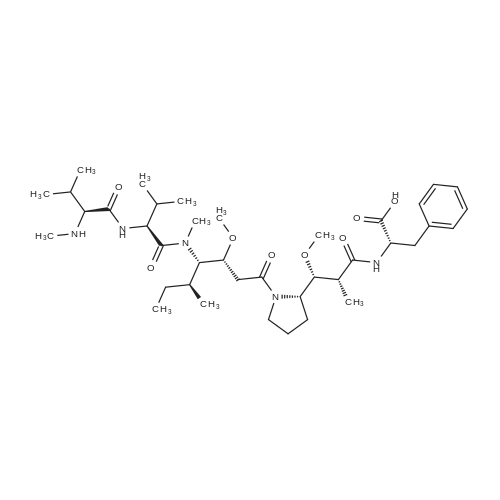
| 描述 | MMAF is a potent auristatin-derived antineoplastic agent, working by inhibition of tubulin polymerization[1]. Different from its analogue MMAE, it has attenuated cytotoxicity due its charged C-terminal phenylalanine. MMAF exhibited cytotoxicity in Karpas 299, H3396, 786-O and Caki-1 cells with IC50 values of 119nM, 105nM, 257nM and 200nM after 96-hour treatment[2]. For the high toxicity of MMAF, it is usually used as the payload of ADCs (antibody-drug conjugates), such as combination with antibody-drug conjugates such as vorsetuzumab mafodotin or SGN-CD19A[3]. Through the link to specific antibody, the selectivity and potency of MMAF could be proved. For example, the ADC cAC10-L4-MMAF4 (anti-CD30) showed cytotoxicity to Karpas 299 cells with IC50 value of 0.065 nM (compared with 119nM, MMAF alone). Intravenous injection with cAC10-L4-MMAF4 at dose of 2mg/kg almost suppressed the median tumor growth in SCID mice xenograft Karpas 299 human ALCL tumors. And the survival was significantly prolonged when the mice were dosed of 8mg/kg cAC10-L4-MMAF4[2]. | ||
| 作用机制 | MMAF is an auristatin derivate which can inhibi tubulin polymerization and destabilize microtubule structure.[1] | ||
| 临床研究 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT号 | 适应症或疾病 | 临床期 | 招募状态 | 预计完成时间 | 地点 |
| NCT02064387 | Multiple Myeloma | Phase 1 | Active, not recruiting | September 28, 2020 | United States, Massachusetts ... 展开 >> GSK Investigational Site Boston, Massachusetts, United States, 02215 United States, Michigan GSK Investigational Site Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States, 48109 United States, Missouri GSK Investigational Site Saint Louis, Missouri, United States, 63110 United States, New York GSK Investigational Site New York, New York, United States, 10065 United States, North Carolina GSK Investigational Site Chapel Hill, North Carolina, United States, 27599-7600 United States, Pennsylvania GSK Investigational Site Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States, 19104 United States, Texas GSK Investigational Site Dallas, Texas, United States, 75390-8565 United States, Washington GSK Investigational Site Seattle, Washington, United States, 98109 Canada, British Columbia GSK Investigational Site Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, V5Z 1M9 Canada, Ontario GSK Investigational Site Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M5G 2M9 United Kingdom GSK Investigational Site London, United Kingdom, NW1 2BU GSK Investigational Site Manchester, United Kingdom, M20 4BX 收起 << |
| NCT01672775 | Carcinoma, Renal Cell ... 展开 >> Renal Cell Carcinoma of Papillary Histology Renal Cell Carcinoma With Clear Cell Histology Renal Cell Carcinoma With Non-Clear Cell Histology 收起 << | Phase 1 | Completed | - | United States, Michigan ... 展开 >> Site US00005 University of Michigan Medical Center Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States, 48109 Site US00003 Karmanos Cancer Institute Detroit, Michigan, United States, 48201 United States, New York Site US00004 Roswell Park Cancer Institute Buffalo, New York, United States, 14263 Site US00002 Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, New York, United States, 10065 United States, Washington Site US00001 Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Seattle, Washington, United States, 98109 Canada, Alberta Site CA00006 Cross Cancer Institute Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, T6G 1Z2 Canada, British Columbia Site CA00008 British Columbia Cancer Agency Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, V5Z 4E6 Canada, Ontario Site CA00009 London Health Sciences Centre London, Ontario, Canada, N6A 4L6 Canada, Quebec Site CA00007 Jewish General Hospital Montreal, Quebec, Canada, H3T 1E2 收起 << |
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.37mL 0.27mL 0.14mL |
6.83mL 1.37mL 0.68mL |
13.66mL 2.73mL 1.37mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|