| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
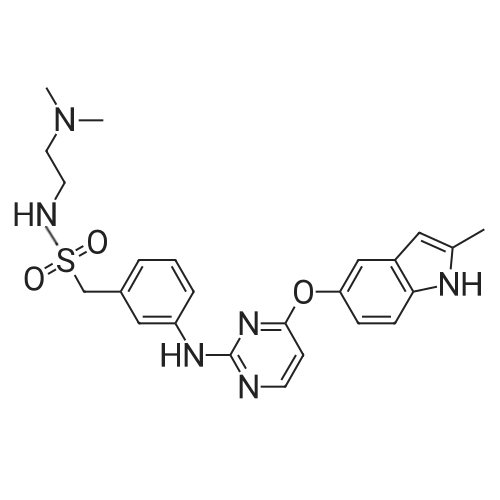
| 描述 | The inhibition of VEGFR-, FGFR-, and CSF1R-mediated pathways may be an effective approach to prevent tumor angiogenesis and immune evasion. Sulfatinib is a potent, small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, FGFR1, and CSF1R with IC50 values of 2, 24, 1, 15, and 4 nM, respectively. It also demonstrated selectivity against fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 and tropomyosin receptor kinase B with IC50 values of 41 and 67 nM, respectively[2]. Sulfatinib inhibited VEGF-induced VEGFR2 phosphorylation in HEK293KDR cells and CSF-1R phosphorylation in RAW264.7 cells with IC50 values of 2 and 79 nM, respectively. It also suppressed VEGF- or FGF-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells with an IC50 less than 50 nM. In nude mice, a single oral dose of sulfatinib inhibited VEGF-stimulated VEGFR2 phosphorylation in lung tissues and suppressed FGFR signaling as evidenced by the upregulation of FGF23 in the plasma[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.08mL 0.42mL 0.21mL |
10.40mL 2.08mL 1.04mL |
20.81mL 4.16mL 2.08mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|