| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
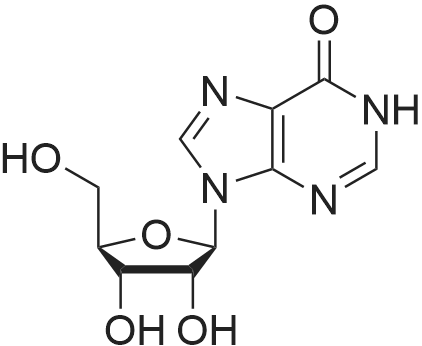
| 描述 | Inosine, a naturally occurring purine nucleoside, has been shown to stimulate axonal growth in cell culture and promote corticospinal tract axons to sprout collateral branches after stroke, spinal cord injury and TBI in rodent models[1]. Inosine-mediated A2AR activation leads to cAMP production with an EC50 of 300.7 μM and to extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 and -2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation with an EC50 of 89.38 μM. Inosine dose-dependently stimulates cAMP production mediated through the A2AR. Inosine dose-dependently induces A2AR-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation[2]. The administration of inosine exerted neuroprotective effects against EAE (experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis) by diminishing clinical signs, including thermal and mechanical hyperalgesia, as well as weight loss typical of the disease. Up-regulation of IL-17 levels in the secondary lymphoid tissues, a result of EAE, was prevented by inosine treatment in EAE mice. Additionally, inosine consistently prevented A2AR up-regulation in the spinal cord, likely, through an ERK1-independent pathway. Graphical Abstract Preventive treatment with inosine inhibits the development and progression of EAE in C57Bl/6 mice. Furthermore, neuroinflammation and demyelinating processes were blocked by inosine treatment[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
3.73mL 0.75mL 0.37mL |
18.64mL 3.73mL 1.86mL |
37.28mL 7.46mL 3.73mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|