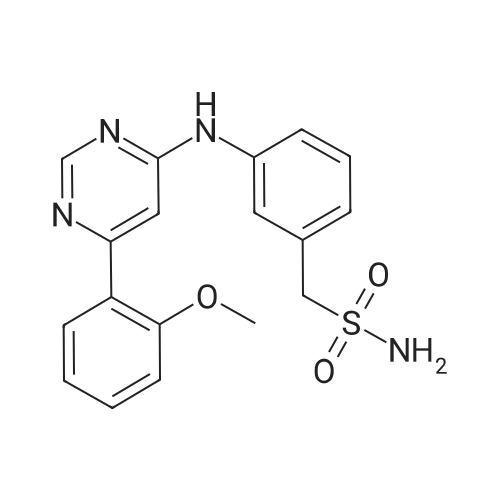
| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
| 描述 | Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a family of evolutionarily conserved serine/threonine kinases that form heterodimers with regulatory cyclin partner proteins. LDC000067 inhibits CDK9 in vitro with an IC50 of 44 ± 10 nM. Its selectivity for CDK9 over other CDKs is in the range of 55-fold (vs. CDK2) to over 230-fold (vs. CDK6 and CDK7). It inhibits in vitro transcription in an ATP-competitive and dose-dependent manner. Transcription assays revealed a half-maximal inhibition of 4 μM for LDC000067 at 100 μM ATP. Notablely, apoptosis induction was most pronounced in cells of leukaemic origin such as THP1 (approximately 45% apoptotic cells at 10 μM LDC000067) and patient-derived blast cells (>60% at 10 μM). Furthermore, repression of mRNA synthesis was first detectable at a concentration of 1 μM, with 50 to 80% repression obtained at a concentration of 10 μM LDC000067. Half-maximal repression by LDC000067 was achieved in the range of 2 to 6 μM. Likewise, treatment with 10 μM LDC000067 caused an 80 to 90% reduction of RNA synthesis in HeLa cells. Luciferase expression decreased in a concentration-dependent manner, with half-maximal repression reached at 2 μM LDC000067[2]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.70mL 0.54mL 0.27mL |
13.50mL 2.70mL 1.35mL |
27.00mL 5.40mL 2.70mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|