| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
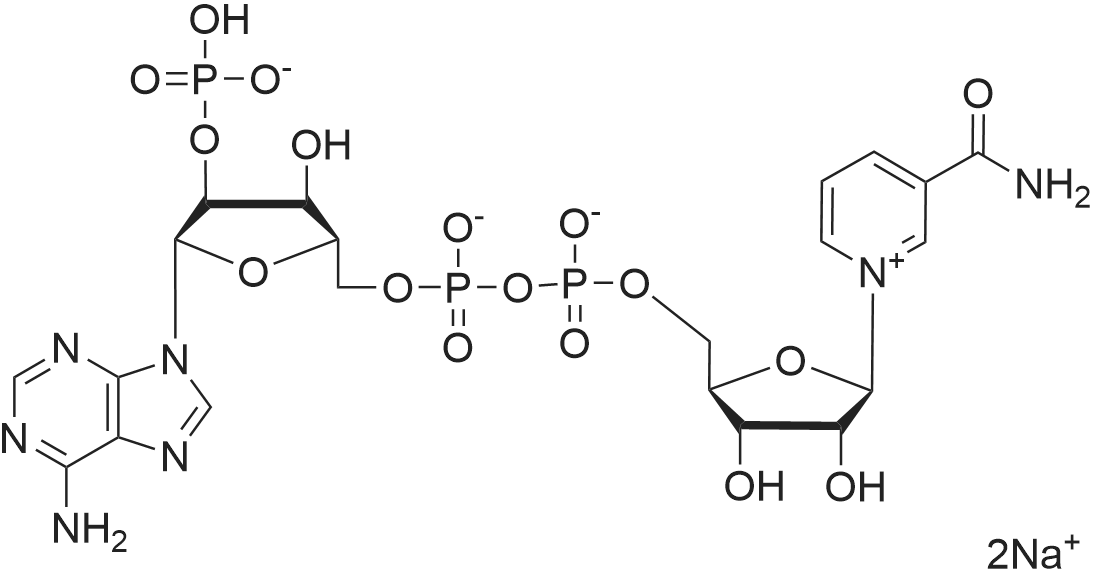
| 描述 | NADP disodium salt (Disodium NADP), a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a redox cofactor. NADP disodium salt is a key cofactor for electron transfer in the metabolism, being alternately oxidized (NADP+) and reduced (NADPH). NADP(+), the oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, plays an essential role as a coenzyme in cellular electron transfer reactions. The concentration of NADP(+) in cytoplasm or organelles is dynamic due to its conversion to many important derivatives[1]. NADP differs from NAD in only the presence of an additional phosphate group esterified to the 2'-hydroxyl group of the ribose at the adenine end and yet NADP is confined with few exceptions to the reactions of reductive biosynthesis, whereas NAD is used almost exclusively in oxidative degradations[2]. NADP is the preferred coenzyme for the oxidative deamination of glutamate by GDH (glutamate dehydrogenase) even though the enzyme is capable of utilizing either coenzyme in vitro[3]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.27mL 0.25mL 0.13mL |
6.35mL 1.27mL 0.64mL |
12.70mL 2.54mL 1.27mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|