| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
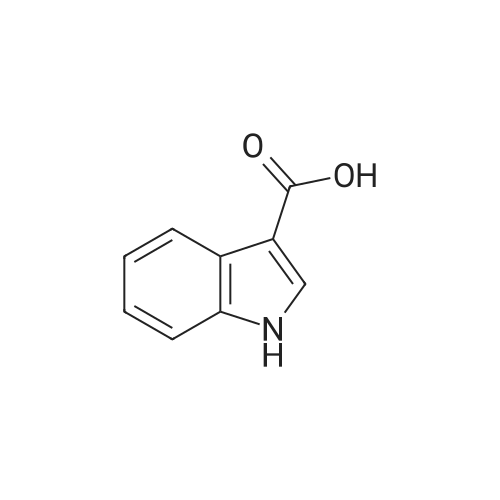
| 描述 | Indole-3-carboxylic acid is a normal urinary indolic tryptophan metabolite and has been found elevated in patients with liver diseases[2]. A novel series of 1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid pyridine-3-ylamides were synthesized and identified to show high affinity and selectivity for 5-HT(2C) receptor. Among them, 1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid[6-(2-chloro-pyridin-3-yloxy)-pyridin-3-yl]-amide (15k) exhibits the highest affinity (IC50=0.5 nM) with an excellent selectivity (>2000 times) over other serotonin (5-HT(1A), 5-HT(2A), and 5-HT(6)) and dopamine (D(2)-D(4)) receptors[3]. After oral administration to mice, I3C (Indole-3-carbinol), in addition to its acid condensation products, is absorbed from the gut and distributed systemically into a number of well-perfused tissues, thus allowing the possibility for some pharmacological activity of the parent compound in vivo[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
6.21mL 1.24mL 0.62mL |
31.03mL 6.21mL 3.10mL |
62.05mL 12.41mL 6.21mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|