| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
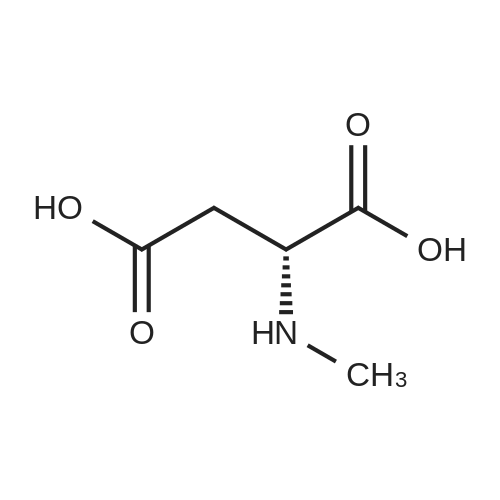
| 描述 | NMDA is a specific agonist for NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. Addition (0.1-10 mM) of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA), one of the agonists for central excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter receptors, exerted a significant augmentation of the adrenal binding independently of the incubation temperature in a concentration-dependent manner[3]. Intracellular glass electrode recordings of single cell in current clamp and two-electrode voltage clamp modes indicate that glutamate (Glu, 0.1-1.0 mM) and NMDA (0.01-1.0 mM) increase electrically induced AP amplitude by hyperpolarising excitation threshold potential (Eth) and prolong AP (action potentials) fast repolarisation phase[4]. NMDA preconditioning reduced the maximal severity 6 displayed in QA(quinolinic acid)-administered mice, inducing protection in 47.6% of mice after QA-induced seizures[5]. Activation of NMDA-receptors is a necessary step of induction of LTP(long-term potentiation), whereas maintenance of LTP related mainly with increase of AMPA(alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate) -EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential)[6]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
6.80mL 1.36mL 0.68mL |
33.98mL 6.80mL 3.40mL |
67.97mL 13.59mL 6.80mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|