| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
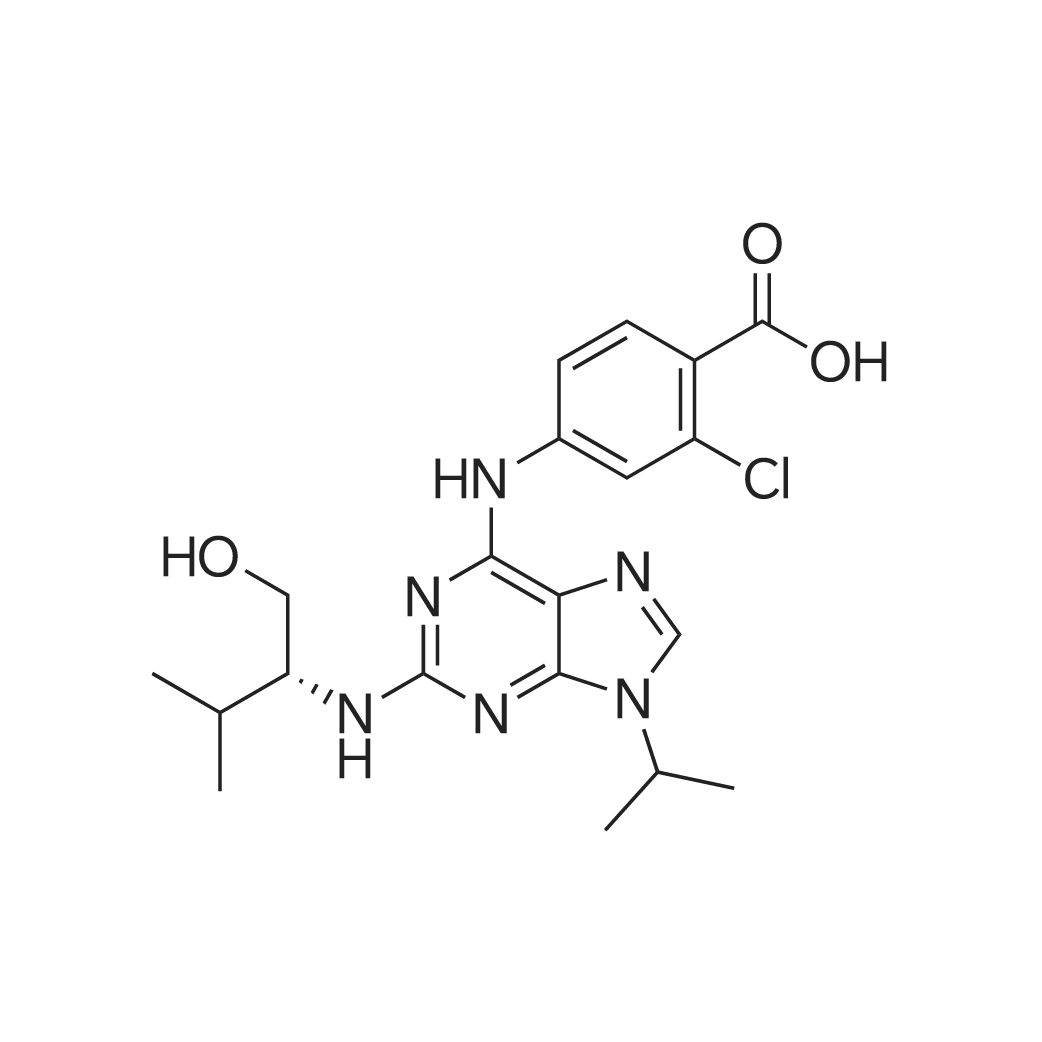
| 描述 | The cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) have a central role in coordinating the eukaryotic cell division cycle, and also serve to integrate diverse growth-regulatory signals[3]. Purvalanol B has been recently optimized for activity against CDK1/cyclin B[4]. While control cultures were composed of mostly multinucleated cells, the inhibitor-treated cultures contained predominantly parasites with only one nucleus, thus indicating parasites were unable to undergo schizogony after the 12-hour exposure to Purvalanol B in DMSO. Synchronized blood stage cultures of P. falciparum at 24 hours post-invasion were treated with 29.8 μM Purvalanol B for 12 hours. Transcript levels of proteasome component C8 were up-regulated in Purvalanol B-treated cultures compared to control cultures. Additionally, subunit of proteasome activator complex, proteasome subunit α type, and thioredoxin reductase 2, the protein levels of which were all up-regulated in treated group. These data indicated that Purvalanol B application decreased the ability of late-stage P. falciparum trophozoites to form multinucleated schizonts and up-regulates proteasome subunits and proteins that contribute to redox homeostasis[5]. | ||
| 作用机制 | Purvalanol B reversibly inhibits CDKs, by competing with ATP for binding to the catalytic site of the kinase. The N6 position of its purine acts as a donor in an essential hydrogen bond between Purvalanol B and the kinase Leu83 residue. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.31mL 0.46mL 0.23mL |
11.55mL 2.31mL 1.15mL |
23.10mL 4.62mL 2.31mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|