| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
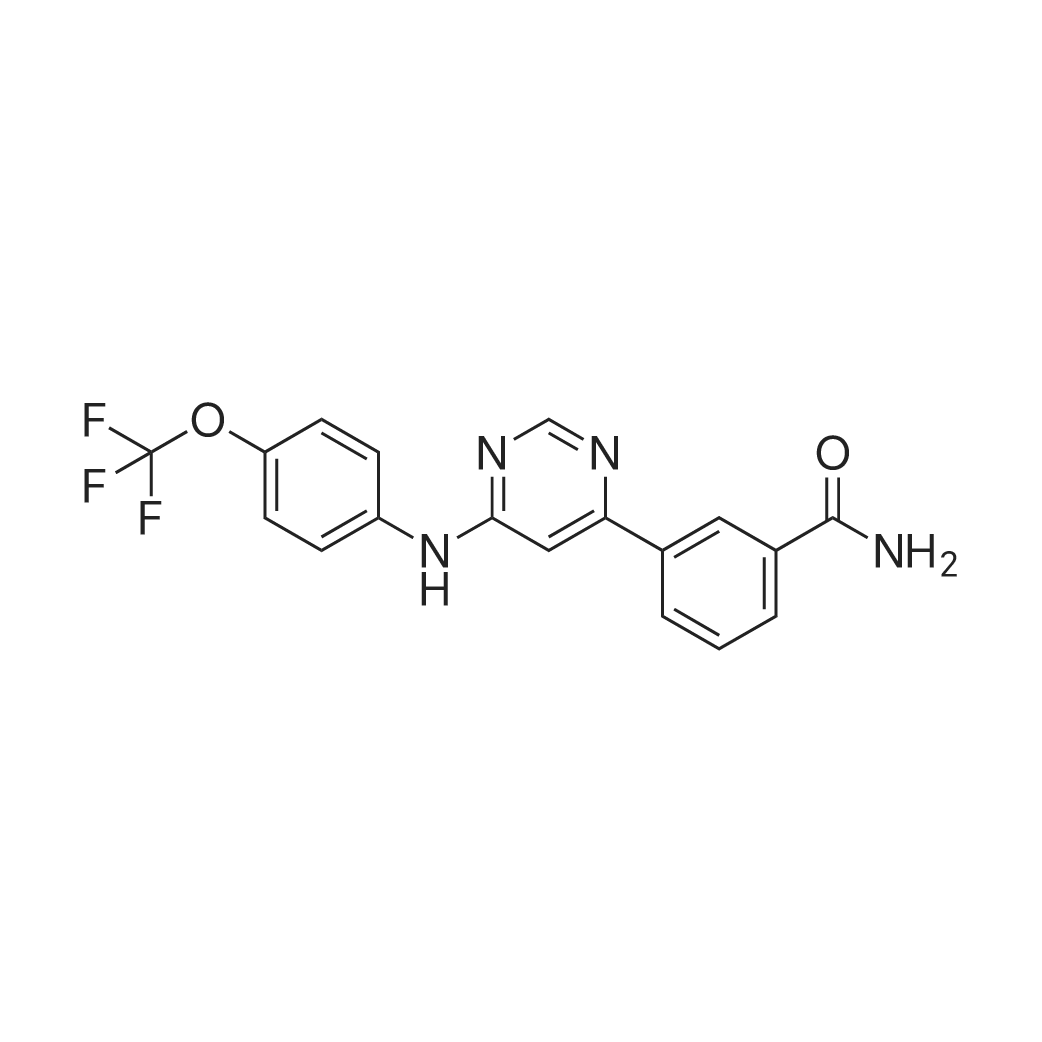
| 描述 | Bcr-Abl is a 210-kDa fusion protein with the combination of the ABL1 (Abelson tyrosine kinase) and the BCR (breakpoint cluster region) , which is validated as a therapeutic target for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia. GNF-2 is a highly selective non-ATP competitive inhibitor of Bcr-Abl. GNF-2 inhibited cell proliferation with an IC50 of 138 nM and cell growth with an IC50 of ~170 nM in Bcr-Abl-expressing cell lines. The cellular tyrosine phosphorylation of Bcr-Abl was inhibited by GNF-2 in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 267 nM. Treatment of Ba/F3.p210 cell lines with 1 μM GNF-2 for 90min significantly decreased the level of phospho-Stat5. Incubation of 1 μM GNF-2 for 48 hours induced apoptotic death in Ba/F3.p210 (wild type and E255V mutant) cells. With the presence of c-Abl SH3 and/or SH2 domains, 10 μM GNF-2 inhibited tyrosine kinase activity of recombinant Abl in vitro. The phosphorylation of CrkII, a well-characterized c-Abl substrate, was inhibited by GNF-2 in a dose-dependent manner from 0.1 to 10 μM in one hour in c-Abl-reconstituted 3T3 cells. The combination of 5 or 10 μM GNF-2 and 1 μM imatinib decreased the number of resistant clones resulted from continuous exposure to 1 μM imatinib by 90% in Ba/F3 cells after 21-day treatment. | ||
| 作用机制 | GNF-2 inhibits tyrosine kinase activity in c-Abl through competing with the myristoyl residue for binding to the myristate-binding pocket. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.67mL 0.53mL 0.27mL |
13.36mL 2.67mL 1.34mL |
26.72mL 5.34mL 2.67mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|