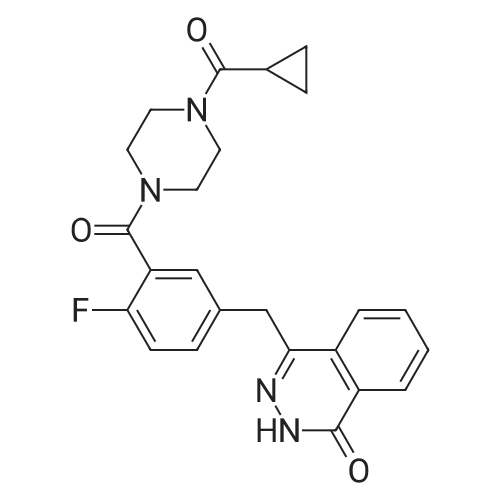
| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
| 描述 | PARP1, also called as Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, is involved in the signaling of DNA damage. It can recognize and bind DNA single or double-strand breaks . Thus it possesses various cellular function, including regulation of apoptosis and chromosome stability, gene amplification and transcription, as well as cell division and differentiation. PARP-2 is the closest homolog of PARP1 (~62% similarity in catalytic domain) and compensates for PARP-1 activity in DNA single-strand break repair[1]. Olaparib, also called as AZD2281 or Ku-0059436, one of the best investigated third-generation PARP inhibitors[2], can potently inhibit both PARP-1 (IC50=5nM) and PARP-2(IC50=1nM)[1]. BRCA1-deficient cell lines, such as MDA-MB-436 and HCC1937, were hypersensitive to olaparib than BRCA1- and BRCA2-proficient cell lines (Hs578T, MDA-MB-231 and T47D). Also olaparib shows good pharmacokinetic profiles, oral bioavailability, as well as activity in vivo[1]. These facilitate olaparib approved for use in recurrent ovarian cancer and germline BRCA HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer[2]. | ||
| 作用机制 | Olaparib occupies the NAD binding pocket at the catalytic site, which has been proposed to trap PARP1 on DNA.[3] | ||
| 细胞研究 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细胞系 | 浓度 | 检测类型 | 检测时间 | 活性说明 | 数据源 |
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.9286 μM | SANGER | ||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.84173 μM | SANGER | ||
| 769-P | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.8466 μM | SANGER | ||
| 临床研究 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT号 | 适应症或疾病 | 临床期 | 招募状态 | 预计完成时间 | 地点 |
| NCT02571725 | Ovarian Cancer ... 展开 >> Fallopian Tube Cancer Peritoneal Neoplasms 收起 << | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | February 2022 | United States, Florida ... 展开 >> Moffitt Cancer Center Recruiting Tampa, Florida, United States, 33612 Contact: Eleni Rokakis, BSN, RN 813-745-3593 Eleni.Rokakis@moffitt.org United States, New Mexico Southwest Gynecologic Oncology Associates Recruiting Albuquerque, New Mexico, United States, 87106 Contact: Karen Finkelstein, MD 505-843-7813 University of New Mexico Comprehensive Cancer Center Recruiting Albuquerque, New Mexico, United States, 87131 Contact: Valerie Parks, RN 505-925-0390 vparks@salud.unm.edu Principal Investigator: Sarah F Adams, MD United States, Ohio The Ohio State University Recruiting Columbus, Ohio, United States, 43210 Contact: David M O'Malley, MD 614-685-6411 Contact: Molly Myers 614-685-6411 molly.myers@osumc.edu United States, Virginia University of Virginia Cancer Center Recruiting Charlottesville, Virginia, United States, 22903 Contact: Anne Gabel 434-982-6657 am7bd@virginia.edu 收起 << |
| NCT03579784 | Advanced Gastric Cancer | Phase 2 | Recruiting | April 30, 2020 | Korea, Republic of ... 展开 >> Seoul National University Hospital Recruiting Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 110-744 Contact: Do-Youn Oh, MD, PhD 82-2-2072-0701 ohdoyoun@snu.ac.kr 收起 << |
| NCT01972217 | Metastatic Castration-resistan... 展开 >>t Prostate Cancer 收起 << | Phase 2 | Active, not recruiting | December 31, 2018 | - |
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.30mL 0.46mL 0.23mL |
11.51mL 2.30mL 1.15mL |
23.02mL 4.60mL 2.30mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|