| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
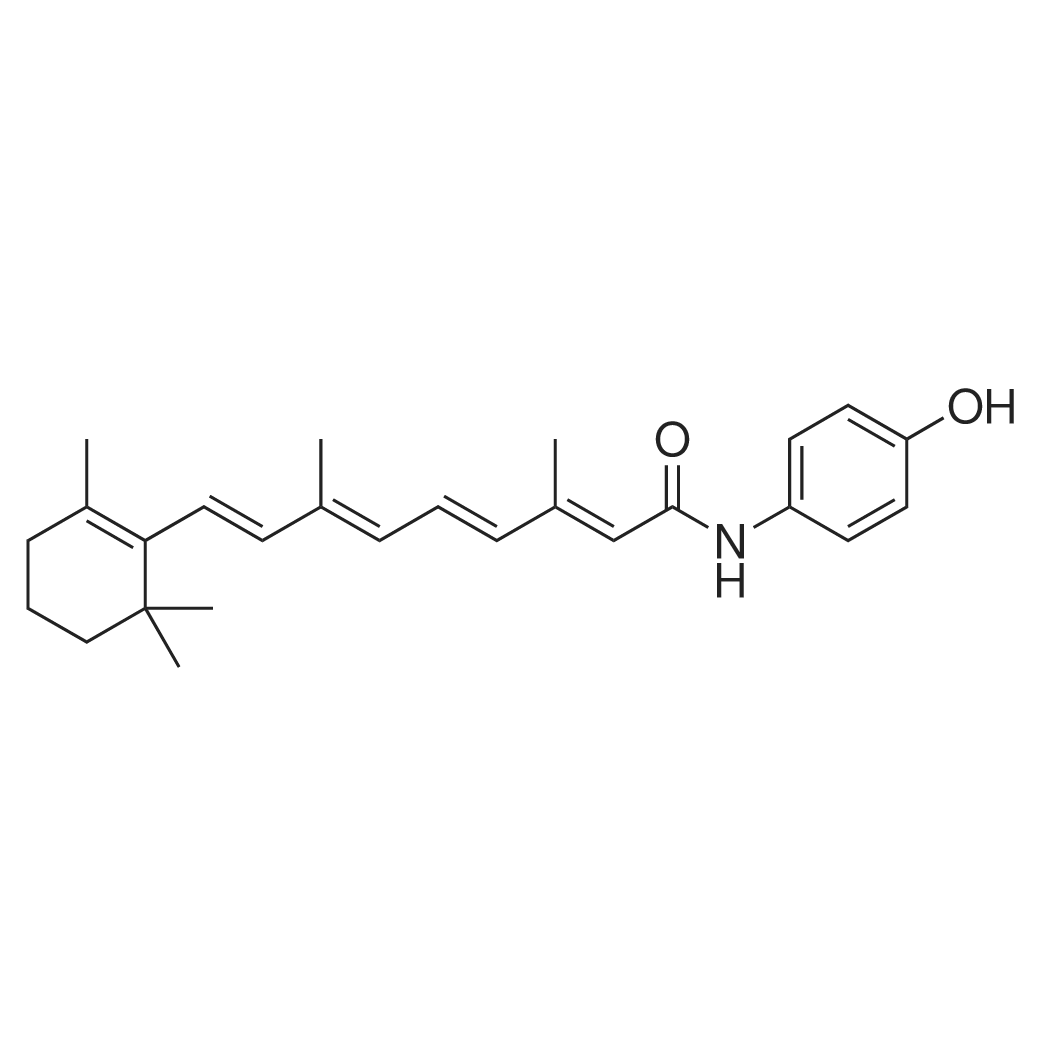
| 描述 | Fenretinide (4-HPR) is a synthetic retinoid deriverative, binding to the retinoic acid receptors (RAR) at concentrations necessary to induce cell death.Fenretinide (4-HPR) demonstrates both immediate and prolonged antitumor effects in specific T-ALL cell lines. It suppresses DES activity in CCRF-CEM leukemia cells dependent on dosage and duration, resulting in increased levels of endogenous cellular dhCer. A rise in dhCer levels is observed in both CCRF-CEM and Jurkat cells with Fenretinide treatment at 3 µM[1]. Ceramide inhibition with fenretinide protects insulin signaling, which prevents lipid-induced reductions in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake[2]. When applied at concentrations over 1 µM, Fenretinide impedes OVCAR-5 cell growth and survival, achieving 70-90% growth suppression at 10 µM. Preincubation with Fenretinide at 1 µM notably reduces OVCAR-5 cell invasion over three days. Furthermore, endothelial cells exposed to 1 µM of 4-HPR do not form tubular structures, instead forming small cell clusters[4]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.55mL 0.51mL 0.26mL |
12.77mL 2.55mL 1.28mL |
25.54mL 5.11mL 2.55mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|