| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
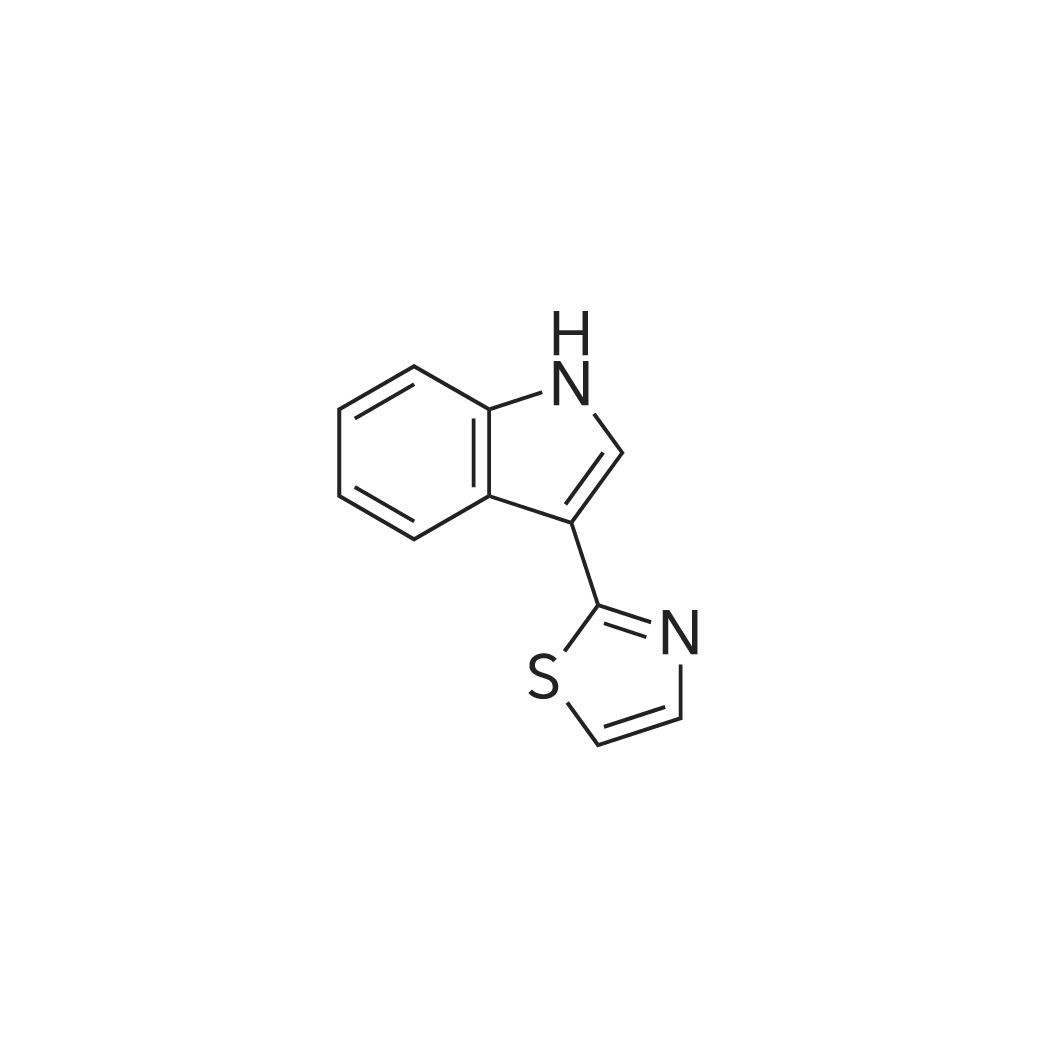
| 描述 | Camalexin is a phytoalexin isolated from Camelina sativa and Arabidopsis (Cruciferae) with antibacterial, antifungal, antiproliferative and anticancer activities. Camalexin can induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. ROS levels, SOD activity, CAT activity, and GSSG levels were significantly enhanced while the GSH level was decreased after treatment of camalexin. Administration of camalexin suppresses xenograft tumor graft growth without obvious toxicity[1]. Camalexin triggers cell shrinkage and phospholipid scrambling of the erythrocyte cell membrane, an effect at least in part depending on Ca2+ entry, as well as staurosporine and chelerythrine sensitive kinase(s) as well as zVAD and zIETD-fmk sensitive caspase(s)[2]. Camalexin reduces cell viability via CD (cathepsin D) and may present as a novel therapeutic agent for treatment of metastatic prostate cancer cells[3]. Treatment of Jurkat cells with camalexin resulted in activation of caspase-8, caspase-9, caspases-3/7, and apoptosis that was detected by the presence of a sub-G1 population of cells, externalization of phosphatidyl serine and decreased mitochondrial membrane potential[4]. Camalexin increased ROS, decreased cell proliferation, and increased apoptosis more significantly in C4-2 and ARCaP-Snail cells as compared to LNCaP and ARCaP-Neo cells, respectively, while normal prostate epithelial cells (PrEC) were unaffected. The ROS scavenger N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) antagonized the effects of camalexin, whereas the addition of exogenous hydrogen peroxide potentiated the effects of camalexin, showing that camalexin is mediating its effects through ROS[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
4.99mL 1.00mL 0.50mL |
24.97mL 4.99mL 2.50mL |
49.94mL 9.99mL 4.99mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|