| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
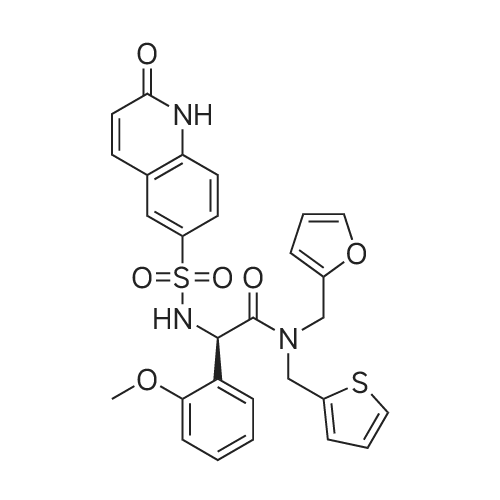
| 描述 | O-GlcNAcylation is an important posttranslational modification governed by a single pair of enzymes-O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and O-GlcNAcase (OGA). These two enzymes mediate the dynamic cycling of O-GlcNAcylation on a wide variety of cytosolic, nuclear and mitochondrial proteins in a nutrient- and stress-responsive fashion[1]. OGT catalyses the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine from UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) to serines and threonines of cytoplasmic, nuclear and mitochondrial proteins, including numerous transcription factors, tumour suppressors, kinases, phosphatases and histone-modifying proteins[2].Biofunctional investigation demonstrated that OGT significantly increased cell growth (p<0.001), clonogenicity (p<0.01), migration and invasion (p<0.05) ability in vitro, and promoted xenograft tumor growth as well as lung metastasis in nude mice[3].OSMI-1 is a cell-permeable OGT inhibitor with an IC50 value of 2.7 μM. OSMI-1 inhibits protein O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAcylation) in several mammalian cell lines without qualitatively altering cell surface N- or O-linked glycans. OSMI-1 (50 μM; 24 hours; CHO cells) treatment decreases the viability by about 50% after 24 hours. OSMI-1 (10-100 μM; 24 hours; CHO cells) treatment reduces global O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAcylation) a dose-dependent manner. OSMI-1 inhibits OGT activity in cells[4].Mammalian and zebrafish toxicity profiles are strikingly similar, and zebrafish can usually serve as an intermediate step between cell-based evaluation and conventional animal testing. The zebrafish model is used to investigate OSM1-1 acute toxicity in vivo. The LC50 of OSM1-1 is 0.031 mg/mL (56 μM, 12 h) and 0.025 mg/mL (45 μM, 24 h) in zebrafish model[5]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.77mL 0.35mL 0.18mL |
8.87mL 1.77mL 0.89mL |
17.74mL 3.55mL 1.77mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|