| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
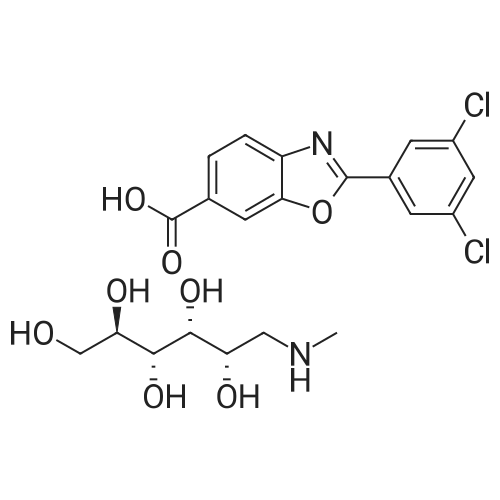
| 描述 | The transthyretin amyloidoses (ATTR) are caused by aggregation of transthyretin (TTR), a natively tetrameric protein involved in the transport of thyroxine and the vitamin A–retinol-binding protein complex[1]. Tafamidis meglumine is a potent and selective transthyretin (TTR) stabilizer, shows comparable potency and efficacy to the mutant homotetramers V30M-TTR, V122I-TTR and wild-type TTR (WT-TTR), with EC50s of 2.7-3.2 μM[1]. It has recently completed Phase II/III trials for the treatment of Transthyretin Type Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (TTR-FAP) and demonstrated a slowing of disease progression in patients heterozygous for the V30M TTR mutation. Patient-derived amyloidogenic variants of TTR, including kinetically and thermodynamically less stable mutants, are also stabilized by tafamidis binding[1]. | ||
| 作用机制 | Tafamidis binds to the weaker dimer–dimer interface of transthyretin . | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
1.99mL 0.40mL 0.20mL |
9.93mL 1.99mL 0.99mL |
19.87mL 3.97mL 1.99mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|