| 生物活性 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 靶点 |
|
||
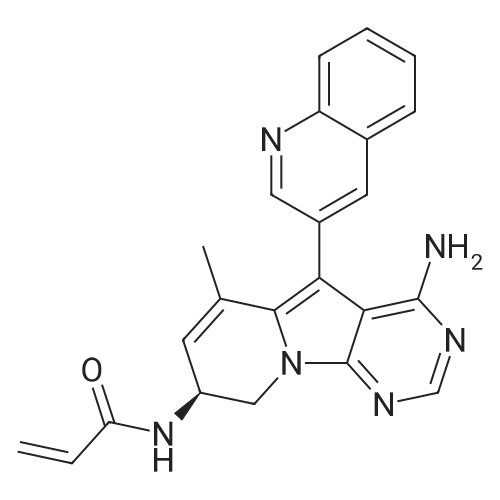
| 描述 | Zipalertinib is a potent, orally active and pan-mutagen-selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a unique scaffold that matches the ATP binding site of the EGFR hinge region and an IC50 value of 1.1-8.0 nM[1][2].Zipalertinib, also known as TAS6417, inhibits EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, leading to caspase activation[1].Zipalertinib exhibits potent inhibition of the most common EGFR mutations (exon 19 deletions and L858R), with the strongest inhibitory effect on cells harbouring EGFR-T790M, a 1st/2nd generation TKI resistance mutation. At concentrations of less than 10 μM, Zipalertinib inhibits cell proliferation and EGFR signalling in NSCLC cell lines carrying or not carrying the common T790M EGFR mutation[2].Zipalertinib covalently modifies the recombinant EGFR exon 20 in-frame insertion mutation at residue 797 cysteine to inhibit EGFR signalling, thereby inhibiting growth and inducing apoptosis in NSCLC cells driven by the EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation[1]. | ||
| 实验方案 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | |
|
1 mM 5 mM 10 mM |
2.52mL 0.50mL 0.25mL |
12.61mL 2.52mL 1.26mL |
25.22mL 5.04mL 2.52mL |
| 参考文献 |
|---|